Stability of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in Nonsupplemented Saliva
Isabel M. Ott
1, Madison S. Strine
1, Anne E. Watkins, Maikel Boot, Chaney C. Kalinich, Christina A. Harden, Chantal B.F. Vogels, Arnau Casanovas-Massana, Adam J. Moore, M. Catherine Muenker, Maura Nakahata, Maria Tokuyama, Allison Nelson, John Fournier, Santos Bermejo, Melissa Campbell, Rupak Datta, Charles S. Dela Cruz, Shelli F. Farhadian, Albert I. Ko, Akiko Iwasaki, Nathan D. Grubaugh
2
, Craig B. Wilen
2, Anne L. Wyllie
2
, and
the Yale IMPACT Research team3
Author affiliations: Yale School of Public Health, New Haven, Connecticut, USA (I.M. Ott, A.E. Watkins, C.C. Kalinich, C.A. Harden, C.B.F. Vogels, A. Casanovas-Massana, A.J. Moore, M.C. Muenker, M. Nakahata, A.I. Ko, N.D. Grubaugh, A.L. Wyllie); Yale School of Medicine, New Haven (M.S. Strine, M. Boot, M. Tokuyama, A. Nelson, J. Fournier, S. Bermejo, M. Campbell, R. Datta, C.S. Dela Cruz, S.F. Farhadian, A.I. Ko, A. Iwasaki, C. Wilen); Howard Hughes Medical Institute, New Haven (A. Iwasaki)
Main Article
Figure 1
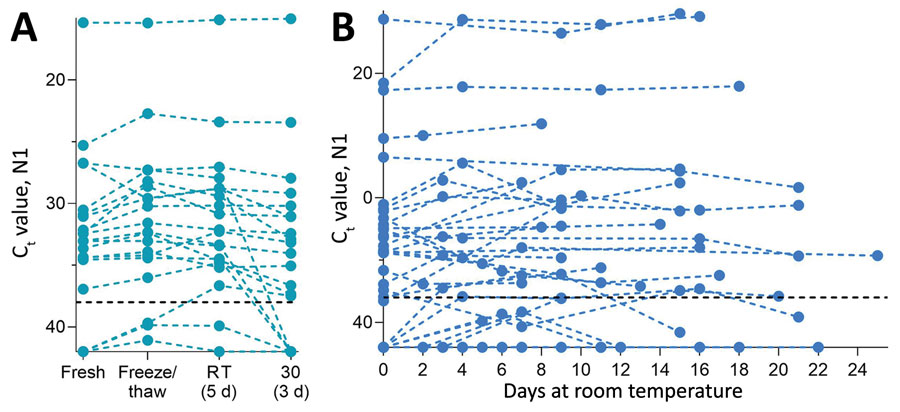
Figure 1. Stability of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) RNA (N1) detection in saliva. A) Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in 20 saliva samples on day of sample collection (fresh) did not significantly change after storage at −80°C (to assess the effect of a freeze/thaw cycle), 3 days at 30°C, or 5 days at RT (recorded as ≈19°C). Detection of N1 remained similar to that of freshly collected samples, regardless of starting Ct value (Pearson r = −0.085, p = 0.518). B) At RT, detection remained stable for up to 25 days. Colored dashed lines track the same sample through different storage conditions. Black horizontal dashed lines represent Ct 38, which we applied as the cutoff to determine sample positivity. Samples that remained not detected after 45 cycles are depicted on the x-axis. Ct, cycle threshold; RT, room temperature.
Main Article
Page created: February 09, 2021
Page updated: March 18, 2021
Page reviewed: March 18, 2021
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
