One Health Genomic Analysis of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase‒Producing Salmonella enterica, Canada, 2012‒2016
Amrita Bharat

, Laura Mataseje, E. Jane Parmley, Brent P. Avery, Graham Cox, Carolee A. Carson, Rebecca J. Irwin, Anne E. Deckert, Danielle Daignault, David C. Alexander, Vanessa Allen, Sameh El Bailey, Sadjia Bekal, Greg J. German, David Haldane, Linda Hoang, Linda Chui, Jessica Minion, George Zahariadis, Richard J. Reid-Smith, and Michael R. Mulvey
Author affiliations: Public Health Agency of Canada, Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada (A. Bharat, L. Mataseje, G. Cox, M.R. Mulvey); University of Manitoba, Winnipeg (A. Bharat, G. Cox, M.R. Mulvey); Public Health Agency of Canada, Guelph, Ontario, Canada (E.J. Parmley, B.P. Avery, C.A. Carson, R.J. Irwin, A.E. Deckert, R.J. Reid-Smith); University of Guelph, Guelph (E.J. Parmley); Public Health Agency of Canada, St. Hyacinthe, Quebec, Canada (D. Daignault); Cadham Provincial Laboratory, Winnipeg (D.C. Alexander); Public Health Ontario Laboratories, Toronto, Ontario, Canada (V. Allen); Horizon Health Network, Saint John, New Brunswick, Canada (S. El Bailey); Laboratoire de Santé Publique du Quebec, Sainte-Anne-de-Bellevue, Quebec, Canada (S. Bekal); Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada (G.J. German); Queen Elizabeth II Health Sciences Centre, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada (D. Haldane); British Columbia Center for Disease Control, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada (L. Hoang); Public Health Laboratory, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada (L. Chiu); University of Alberta, Edmonton (L. Chui); Roy Romanow Provincial Laboratory, Regina, Saskatchewan, Canada (J. Minion); Newfoundland and Labrador Public Health and Microbiology Laboratory, St. John’s, Newfoundland, Canada (G. Zahariadis)
Main Article
Figure 5
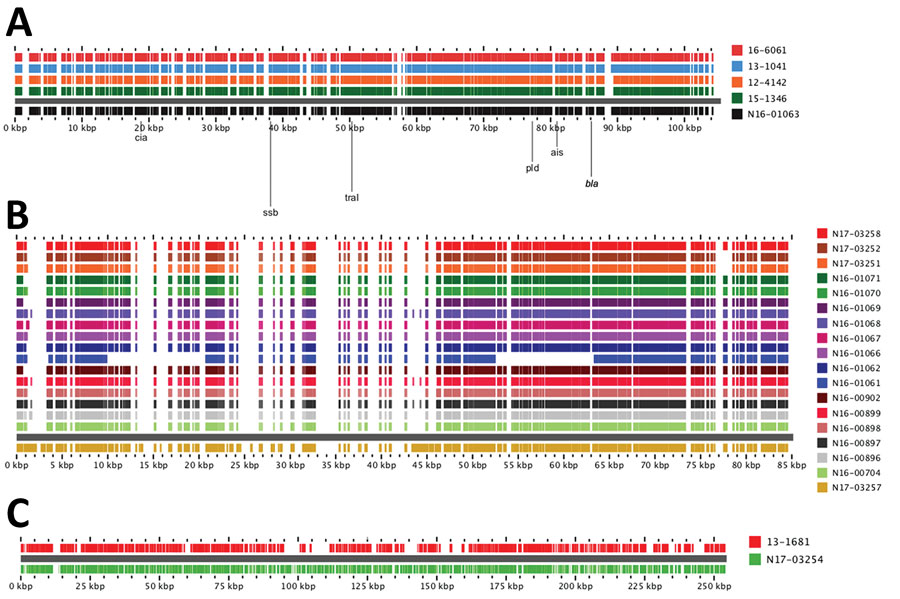
Figure 5. Alignment of Salmonella blaCTX-M plasmids from human and animals/meat sources, Canada. Alignments of blaCTX-M-1 IncI1 (A), blaCTX-M-1 IncN (B), and blaCTX-M-55 IncN (C) plasmids are shown. Plasmids were aligned by using the BLAST feature of the GView server (https://server.gview.ca) and representative closed plasmids (bottom-most plasmid in each alignment) from this study. Animals/meat sample identifications start with the letter N, and human sample identifications start with a 2-digit number.
Main Article
Page created: May 03, 2022
Page updated: June 18, 2022
Page reviewed: June 18, 2022
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
