Volume 28, Number 8—August 2022
Dispatch
Zoonotic Threat of G4 Genotype Eurasian Avian-Like Swine Influenza A(H1N1) Viruses, China, 2020
Figure 2
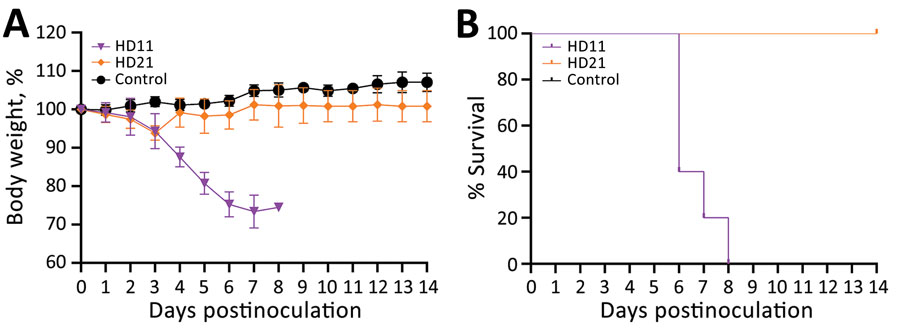
Figure 2. Pathogenicity of 2 G4 Eurasian avian-like influenza A(H1N1) swine isolates from pigs in China in BALB/c mice. A) Body weight change of infected mice. B) Survival curve of infected mice. Two groups of five 6-week-old BALB/c mice were inoculated intranasally with A/swine/Jiangsu/HD11/2020(H1N1) (HD11) or A/swine/Anhui/HD21/2020(H1N1) (HD21) at a dose of 106 50% egg infectious dose/50 µL. Another 5 mice mock-infected with phosphate-buffered saline were served as control. Body weight change and survival rate were recorded daily until 14 days postinoculation, and mice that lost ≥25% of the initial body weight were humanely euthanized.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: June 23, 2022
Page updated: July 20, 2022
Page reviewed: July 20, 2022
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.