Volume 28, Number 8—August 2022
Dispatch
Association of Phylogenomic Relatedness among Neisseria gonorrhoeae Strains with Antimicrobial Resistance, Austria, 2016–2020
Figure 1
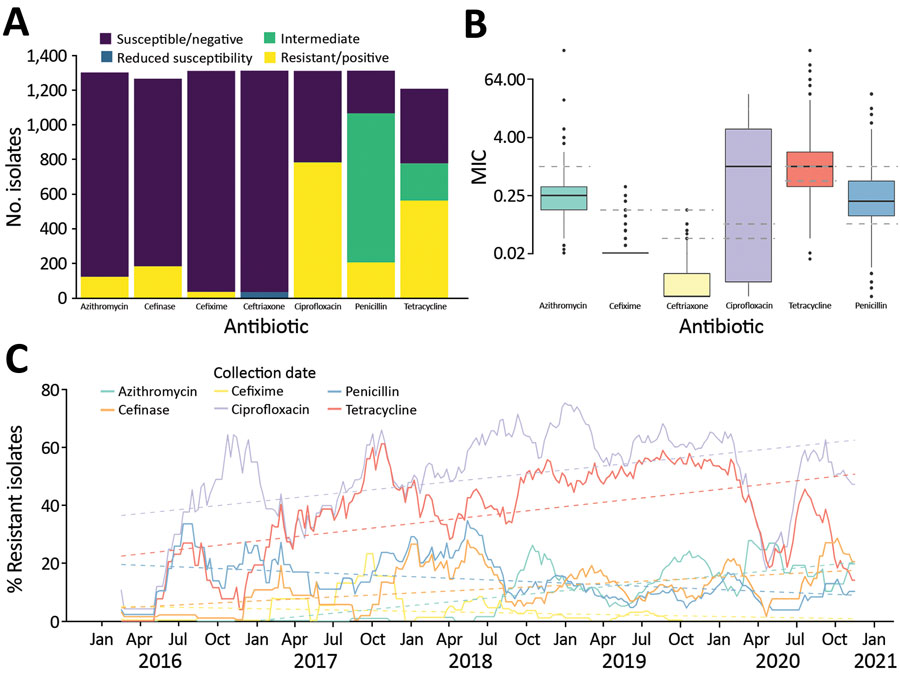
Figure 1. Antimicrobial resistance in 1,318 Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates, Austria, 2016–2020. A) Number of isolates classified as susceptible, intermediate, or resistant. For ceftriaxone, isolates with reduced susceptibility are indicated in blue. For cefinase, β-lactamase producing isolates are indicated as positive (yellow). B) Boxplots of MIC obtained by Etest. Dashed lines indicate the thresholds used to classify the isolates as susceptible, intermediate, or resistant for ciprofloxacin, tetracycline, and penicillin, as susceptible or resistant for azithromycin, cefixime, and as susceptible, reduced susceptibility, or resistant for ceftriaxone. Horizontal lines within boxes indicate median, box tops and bottoms indicate quartiles 1 and 3, and dots indicate potential outliers. C) Evolution of the frequency of resistant isolates over time. Plain lines indicate the 13-week moving average of the percentage of isolates classified as resistant. Trends over time (obtained by linear regression) are represented by the dashed lines.