Volume 28, Number 8—August 2022
Dispatch
Association of Phylogenomic Relatedness among Neisseria gonorrhoeae Strains with Antimicrobial Resistance, Austria, 2016–2020
Figure 2
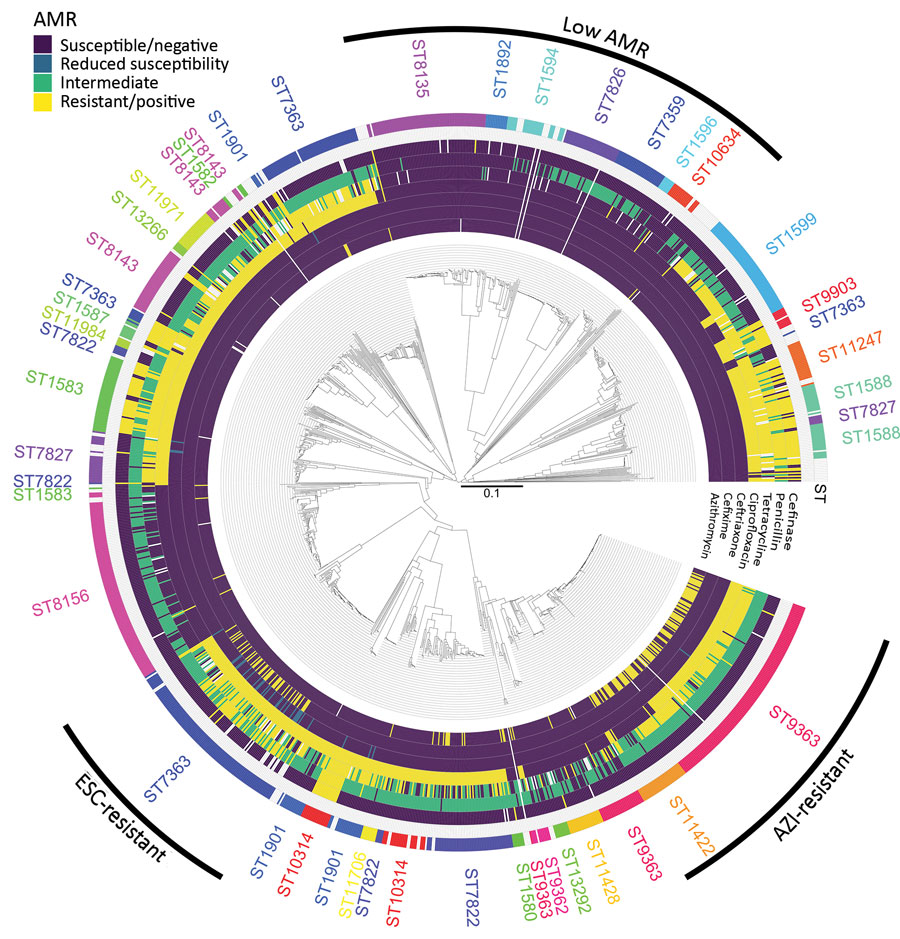
Figure 2. Correlation between population structure and antimicrobial resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates, Austria, 2016–2020. Dendrogram was computed from the distance matrix of the core-genome multilocus sequence typing analysis (N = 1,304). Rims indicate the isolate classification as susceptible, intermediate, or resistant. For ceftriaxone, isolates with reduced susceptibility are indicated in blue. For cefinase, β-lactamase producing isolates are indicated as positive (yellow). The outer rim indicates sequence types corresponding to >2 consecutive isolates. Three branches with specific antimicrobial resistance patterns are indicated. AMR, antimicrobial resistance; AZI, azithromycin; ESC, extended-spectrum cephalosporin.
Page created: June 23, 2022
Page updated: July 20, 2022
Page reviewed: July 20, 2022
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.