Plasmodium falciparum pfhrp2 and pfhrp3 Gene Deletions in Malaria-Hyperendemic Region, South Sudan
Irene Molina-de la Fuente
1, María José Sagrado Benito
1
, Laurence Flevaud, Janet Ousley, Harriet Akello Pasquale, Ahmed Julla, Abdirashid M. Abdi, Buai Tut Chol, Bakri Abubakr, Agustín Benito

, Cristian Casademont, Carolina Nanclares, and Pedro Berzosa
Author affiliations: Institute of Health Carlos III, Madrid, Spain (I. Molina-de la Fuente); Alcala University, Madrid (I.M. de la Fuente, A. Benito, P. Berzosa); Médecins Sans Frontières, Barcelona, Spain (M.J.S. Benito, L. Flevaud, C. Casademont, C. Nanclares); Médecins Sans Frontières, New York, New York, USA (J. Ousley); National Malaria Control Program, Ministry of Health, Juba, South Sudan (H.A. Pasquale, A. Julla); Médecins Sans Frontières, Juba (A.M. Abdi, B.T. Chol); Médecins Sans Frontières, Nairobi, Kenya (B. Abubakr); Centro de Investigación Biomedica en Red de Enfermedades Infecciosas, Madrid (A. Benito, P.J.B. Diaz)
Main Article
Figure 2
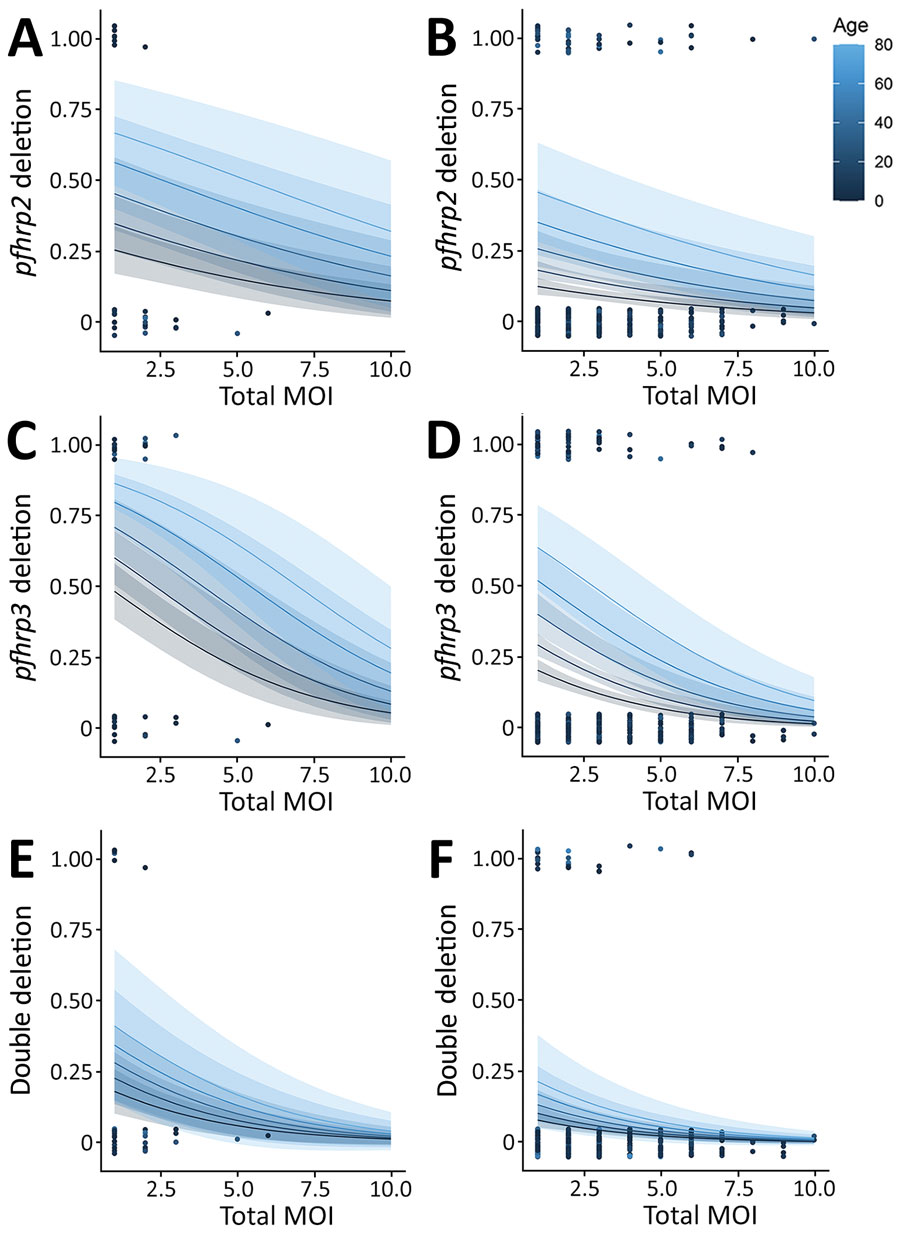
Figure 2. Multivariable regression model of Plasmodium falciparum pfhrp2 deletions (A), pfhrp3 deletions (B), and double deletions (C) in malaria-hyperendemic region, South Sudan. Panels A, C, and E indicate uncomplicated malaria; panels B, D, and F, severe malaria. The models combined 2 continuous variables: age of the patient, represented with different colors, and total MOI, represented in x-axis, with the binary response variable (presence of deletion). Probability of deletion (y-axis) was considered a binary outcome variable. The quality of the model was evaluated by the likelihood ratio method. The model was significant (p value<0.01) for pfhrp2 and pfhrp3 deletion and pfhrp2 and pfhrp3 double deletion. Each dot represents 1 sample. MOI, multiplicity of infection.
Main Article
Page created: November 17, 2022
Page updated: December 22, 2022
Page reviewed: December 22, 2022
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
