Volume 29, Number 10—October 2023
Dispatch
Pseudomonas aeruginosa High-Risk Sequence Type 463 Co-Producing KPC-2 and AFM-1 Carbapenemases, China, 2020–2022
Figure 2
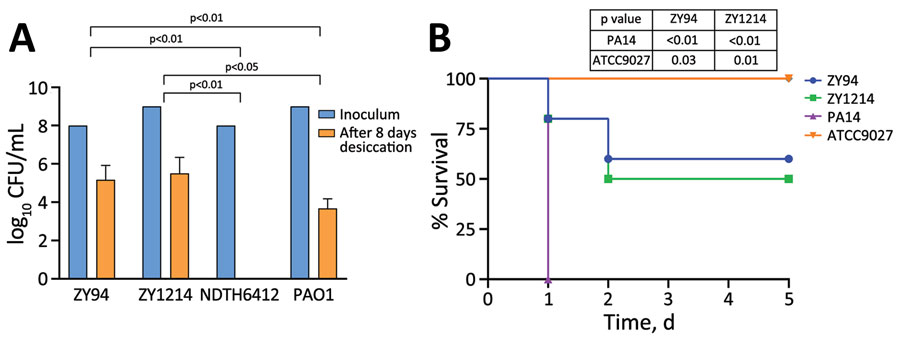
Figure 2. Desiccation tolerance and virulence analyses of Pseudomonas aeruginosa high-risk sequence type 463 co-producing KPC-2 and AFM-1 carbapenemases, China, 2020–2022. A) Carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa strains ZY94 and ZY1214 isolated from hospital patients in China were evaluated for desiccation tolerance. Results are given as mean (SD) CFU/mL for each isolate before and after 8 days of desiccation. Laboratory reference strain PAO1 and P. aeruginosa NDTH6412, which belongs to high-risk international sequence type 235, were used as controls. B) Virulence was determined by using Kaplan-Meier survival curves of mice intraperitoneally challenged with 1 × 107 CFUs of strain ZY94 or ZY1214, hypervirulent strain PA14, or nonvirulent P. aeruginosa strain ATCC9027. Mice (10 per group) were monitored for 5 days and the number of dead mice was assessed each day. Mantel-Cox log rank tests were used to calculate p values for survival curve comparisons between the different strains. AFM, Alcaligenes faecalis metallo-β-lactamase; CFUs, colony forming units; KPC, Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
2These senior authors contributed equally to this article.