Volume 29, Number 6—June 2023
Dispatch
Replication of Novel Zoonotic-Like Influenza A(H3N8) Virus in Ex Vivo Human Bronchus and Lung
Figure 1
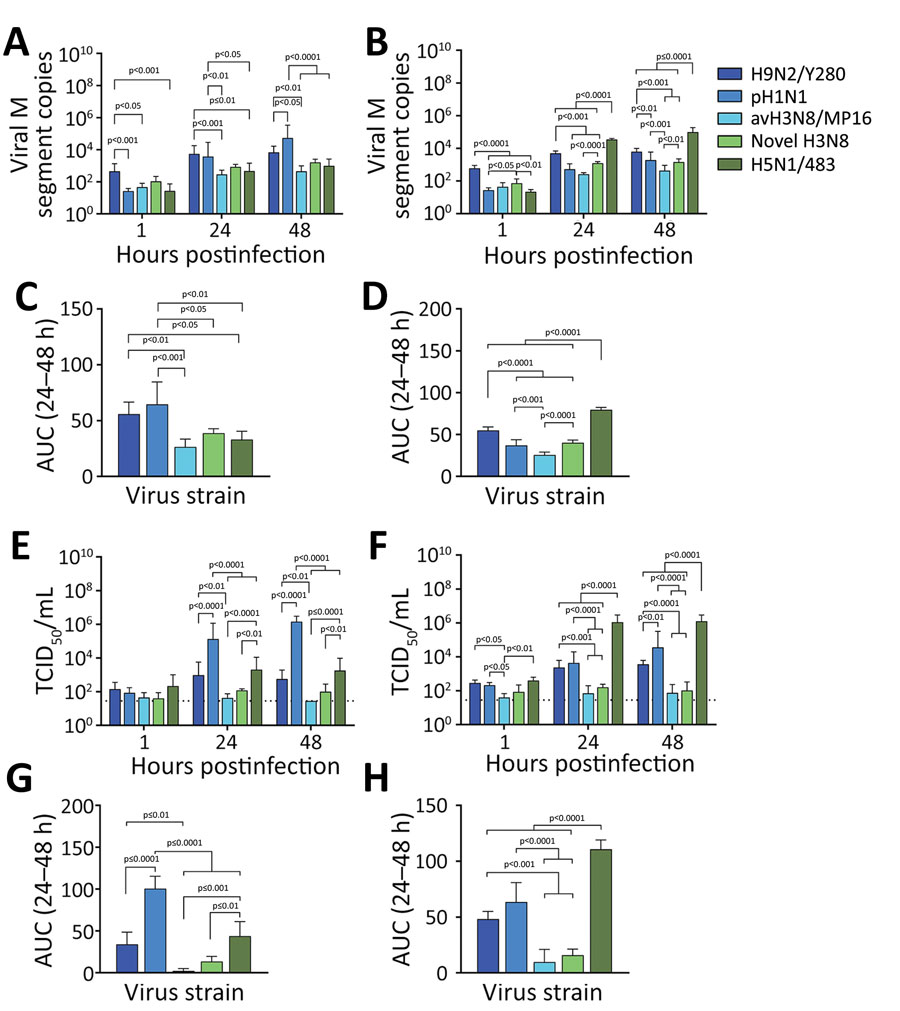
Figure 1. Comparative replication competence of zoonotic-like influenza A(H3N8) viruses isolated from chicken and other human and avian viruses in ex vivo cultures of human bronchus and lung tissue. Viral M segment RNA copies (A, B) and viral titers (E, F) in culture supernatants were collected at 1, 24, and 48 hours postinfection with H9N2/Y280, pH1N1, avH3N8/MP16, novel H3N8, or H5N1/483 viruses and measured by quantitative reverse transcription PCR (A, B) and TCID50 (E, F). C, D) Viral load from panels A and B by virus strain. G, H) Viral titers from panels E and F by virus strain. Data are geometric mean +SD. Statistical analysis was performed using 2-way (A, B, E, F)or 1-way (C, D, G, H) analysis of variance followed by Tukey posttest; p<0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. Detailed information on viruses used in study is provided in the Appendix. AUC, area under the curve; M, matrix; TCID50, 50% tissue culture infectious dose.