Novel Avian Influenza Virus (H5N1) Clade 2.3.4.4b Reassortants in Migratory Birds, China
Jing Yang
1, Chunge Zhang
1, Yue Yuan
1, Ju Sun
1, Lu Lu
1, Honglei Sun, Heting Sun, Dong Chu, Siyuan Qin, Jianjun Chen, Chengbo Zhang, Xiyan Hao, Weifeng Shi, Wenjun Liu, George F. Gao, Paul Digard, Samantha Lycett, and Yuhai Bi

Author affiliations: Institute of Microbiology, Center for Influenza Research and Early-warning (CASCIRE), Chinese Academy of Sciences–The World Academy of Sciences Center of Excellence for Emerging Infectious Diseases, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China (J. Yang, Chunge Zhang, J. Sun, W. Liu, G.F. Gao, Y. Bi); University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing (J. Yang, Chunge Zhang, W. Liu, G.F. Gao, Y. Bi); Shandong First Medical University, Taian, China (Y. Yuan, W. Shi, Y. Bi); Shanxi Agricultural University, Taigu, China (J. Sun, Y. Bi); University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK (L. Lu, P. Digard, S. Lycett); China Agricultural University, Beijing (Honglei Sun); State Forestry and Grassland Administration, Shenyang, China (Heting Sun, D. Chu, S. Qin); Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan, China (J. Chen); Ordos Forestry and Grassland Development Center, Ordos, China (Chengbo Zhang); Hohhot Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Hohhot, China (X. Hao)
Main Article
Figure 1
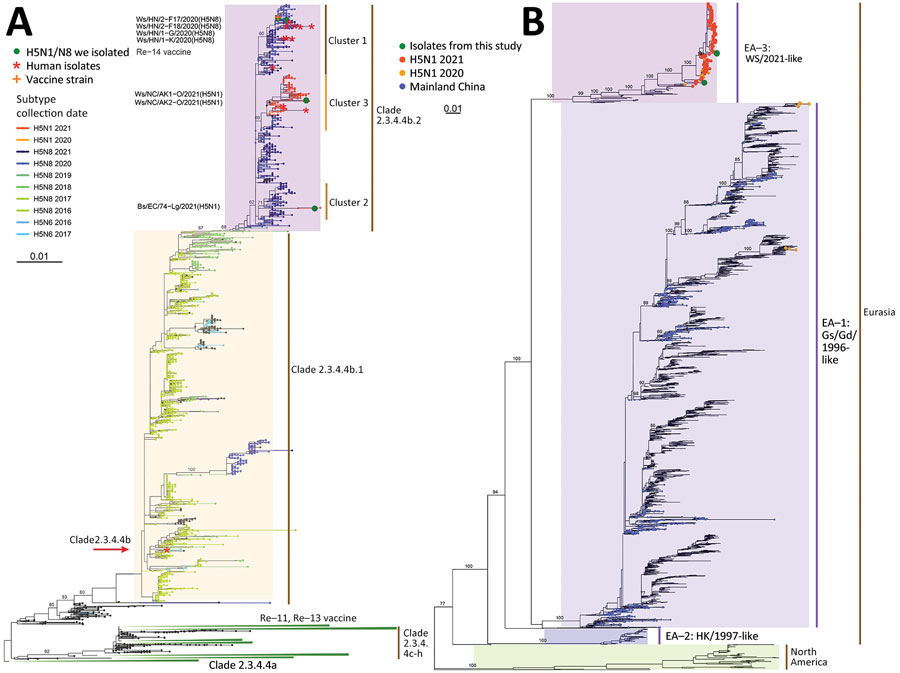
Figure 1. Phylogenetic trees for hemagglutinin genes of clade 2.3.4.4 H5Ny and neuraminidase genes of global H5N1 avian influenza viruses. A) Phylogeny of hemagglutinin genes of global clade 2.3.4.4 H5Ny avian influenza viruses. Solid green circles indicate H5N1 and H5N8 viruses from wild birds isolated in China; sequence names are listed next to corresponding circles. Red asterisks indicate human isolates. H5 vaccine seed strains used in mainland China are listed near the corresponding clades; orange cross indicates Re-14 vaccine. The major H5Ny subtypes within clade 2.3.4.4b are colored by their subtypes and collection dates. Clade 2.3.4.4b was divided into clade 2.3.4.4b.1 and clade 2.3.4.4b.2 because of >2.7% average pairwise nucleotide distance and >60% support for the 2 subclades. B) Phylogeny of global H5N1 neuraminidase genes. Colored circles indicate the novel H5N1 viruses from this study, H5N1 viruses from mainland China, and H5N1 viruses isolated in 2020 and 2021. Numbers on branches represent bootstrap support values for some major clades. Scale bar indicates number of nucleotide substitutions per site. Full phylogenetic trees of hemagglutinin genes of global H5Ny and neuraminidase genes of global H5N1 are provided at https://github.com/judyssister/globalH5N1_2021.
Main Article
Page created: April 17, 2023
Page updated: May 17, 2023
Page reviewed: May 17, 2023
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
