Volume 30, Number 1—January 2024
Dispatch
Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Neuraminidase Inhibition Antibodies in Healthy Adults after Exposure to Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09
Figure
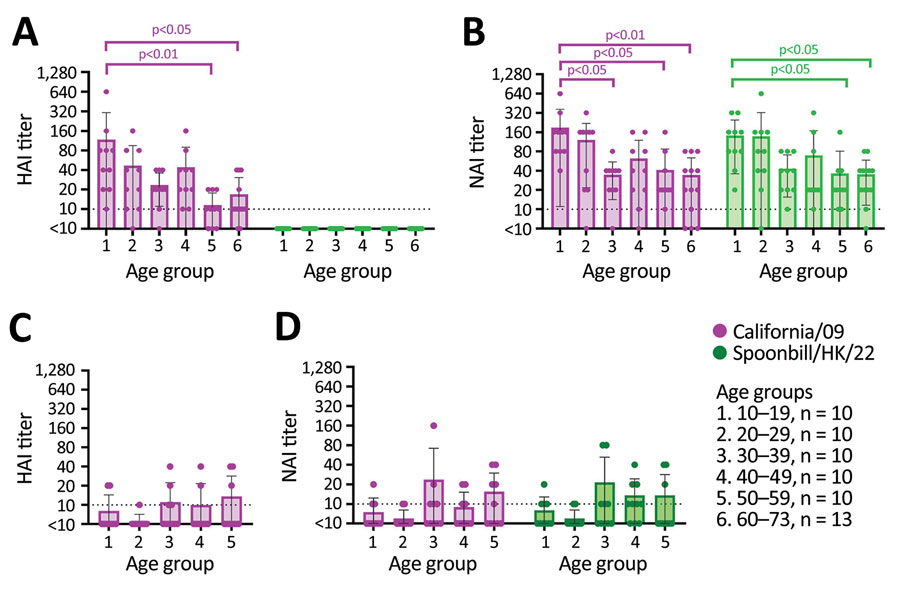
Figure. Age-stratified HAI and NAI antibody responses to influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 (California/09) and A(H5N1) (Spoonbill/HK/22) viruses in serum samples collected from healthy adults in 2020 and 2009, Hong Kong, China. A, B) Results for serum samples of 63 healthy adults collected in 2020. C, D) Results for serum samples of 50 healthy adults collected in 2009. The assay detection limit was 1:10, and samples with antibody below the detection limit were assigned an arbitrary antibody titer of 5, which is used to calculate geometric mean titer. The HAI and NAI titers across different age groups were compared using Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn’s multiple comparison test. HAI, hemagglutination inhibition; NAI, neuraminidase inhibition.
1These senior authors contributed equally to this article.