Volume 30, Number 12—December 2024
Dispatch
Transboundary Movement of Yezo Virus via Ticks on Migratory Birds, Japan, 2020–2021
Figure 2
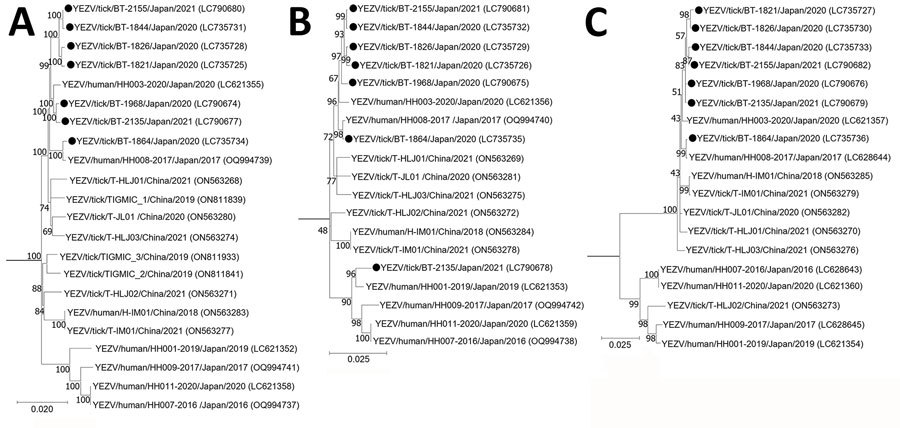
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis of Yezo virus strains in study of transboundary movement of Yezo virus via ticks on migratory birds, Japan, 2020–2021. Trees were constructed by using the maximum-likelihood method in MEGA X (https://www.megasoftware.net) and 1,000 bootstrap replicates for nucleotide sequences. A) Large segment; B) medium segment; C) small segment. Black circles indicate sequences from this study. The number at each branch indicates the bootstrap value. GenBank accession numbers for nucleotide sequences are shown in parentheses. Sulina virus IxriSL16-01 was used as the outgroup to determine the root of Yezo virus trees but is not shown. Scale bars indicate nucleotide substitutions per site.
Page created: November 15, 2024
Page updated: November 26, 2024
Page reviewed: November 26, 2024
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.