Volume 30, Supplement—October 2024
SUPPLEMENT ISSUE
Articles
Genomic Epidemiology of Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in Kenya, Uganda, and Jordan
Figure 2
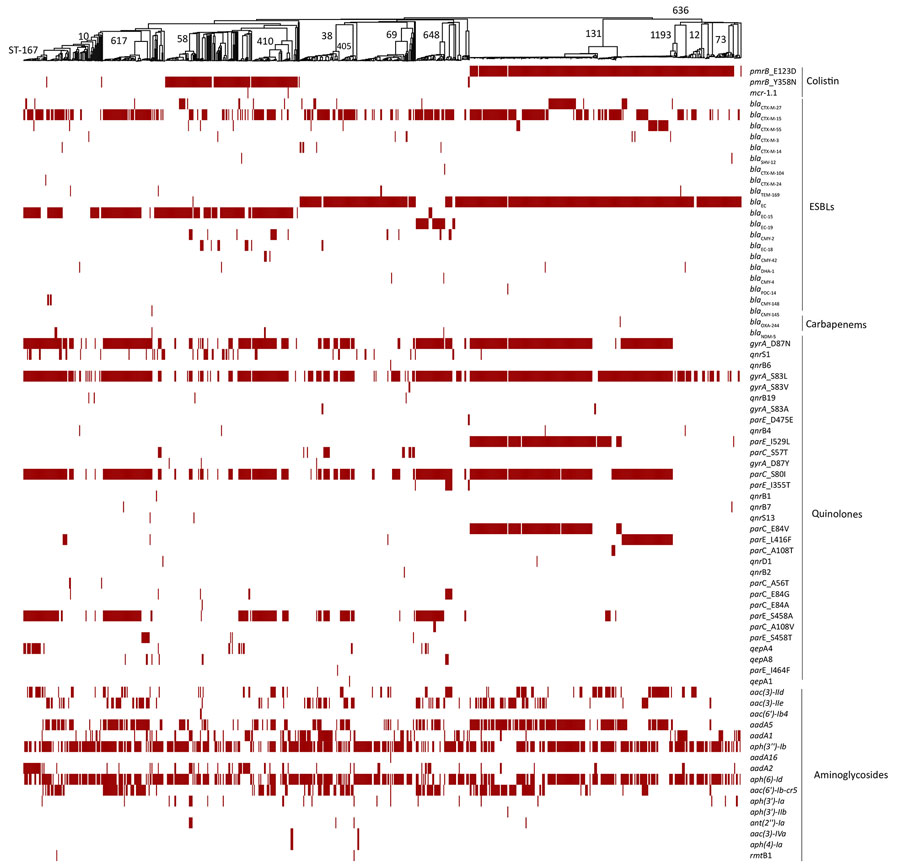
Figure 2. Comprehensive distribution of antimicrobial-resistance genes in 785 Escherichia coli isolates from Kenya, Uganda, and Jordan. Antimicrobial-resistance genes associated with nonsusceptibility to various antibiotic classes (polymyxins, third- and fourth-generation cephalosporins, carbapenems, phenicols and quinolones, and aminoglycosides) for each isolate are labeled for presence (red) or absence (white). The presence or absence of gene(s) is mapped onto a neighbor-joining tree curated from its minimum-spanning tree. The major high-risk STs are labeled on the neighbor-joining tree. ST, sequence type.
Page created: October 30, 2024
Page updated: November 11, 2024
Page reviewed: November 11, 2024
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.