Detection of Nucleocapsid Antibodies Associated with Primary SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Unvaccinated and Vaccinated Blood Donors
Eduard Grebe
1
, Mars Stone
1, Bryan R. Spencer, Akintunde Akinseye, David J. Wright, Clara Di Germanio, Roberta Bruhn, Karla G. Zurita, Paul Contestable, Valerie Green, Marion C. Lanteri, Paula Saa, Brad J. Biggerstaff, Melissa M. Coughlin, Steve Kleinman, Brian Custer, Jefferson M. Jones, and Michael P. Busch
Author affiliations: Vitalant Research Institute, San Francisco, California, USA (E. Grebe, M. Stone, C. Di Germanio, R. Bruhn, K.G. Zurita, B. Custer, M.P. Busch); University of California, San Francisco (M. Stone, R. Bruhn, M.C. Lanteri, B. Custer, M.P. Busch); American Red Cross, Rockville, Maryland, USA (B.R. Spencer, P. Saa); Westat, Rockville (A. Akinseye, D. Wright); QuidelOrtho, Rochester, New York, USA (P. Contestable); Creative Testing Solutions, Tempe, Arizona, USA (V. Green, M.C. Lanteri); Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Fort Collins, Colorado, USA (B.J. Biggerstaff); Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia, USA (M.M. Coughlin, J.M. Jones); University of British Columbia, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada (S. Kleinman)
Main Article
Figure 3
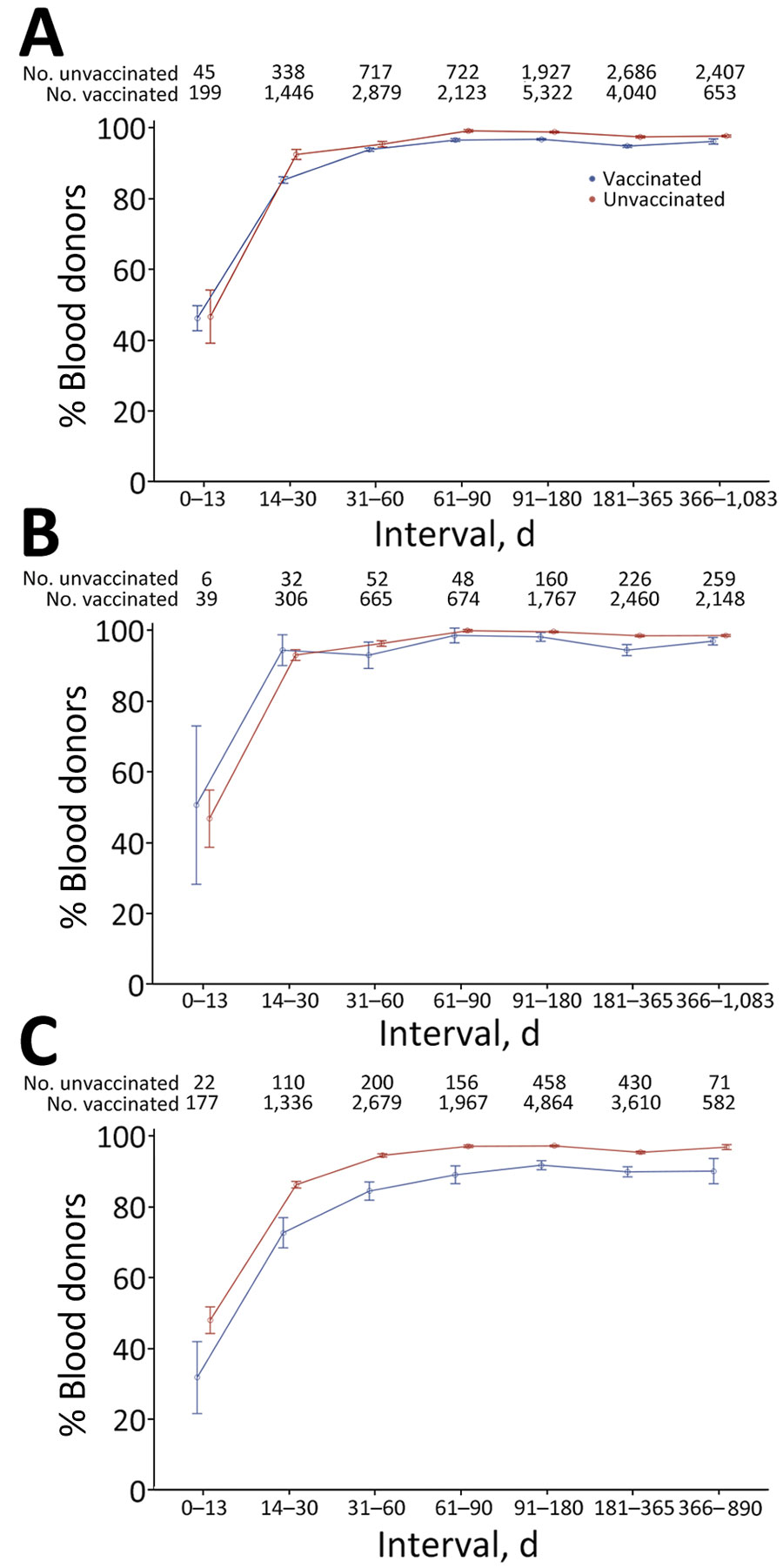
Figure 3. Sensitivity of nucleocapsid antibody serologic tests by time from swab-confirmed infection to sample collection in vaccinated and unvaccinated blood donors, using the manufacturer’s recommended cutoff, United States, July 2021–December 2022. The percentage of donors showing reactivity in first or subsequent samples after swab-confirmed infection is shown. A) Reactive proportions stratified by vaccination status at the time of infection. B) Reactive proportions for infections in unvaccinated donors stratified by reported symptoms. C) Reactive proportions for infections in vaccinated donors, stratified by reported symptoms. To account for multiple observations per time bin, observations were weighted so that donors were equally weighted within each time bin, regardless of the number of observations. Error bars indicate median and maximum durations of follow-up for each group.
Main Article
Page created: June 10, 2024
Page updated: June 11, 2025
Page reviewed: June 11, 2025
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
