Volume 30, Number 9—September 2024
Synopsis
Clinical Significance, Species Distribution, and Temporal Trends of Nontuberculous Mycobacteria, Denmark, 1991–2022
Figure 2
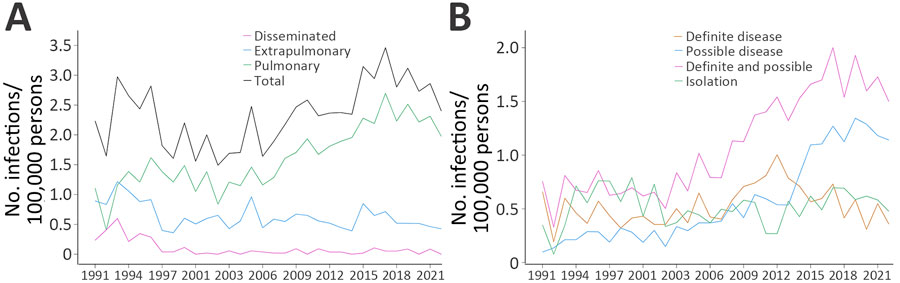
Figure 2. Annual incidence rates (infections/100,000 persons) of unique patients with a first culture positive for nontuberculous mycobacteria, by disease localization (A) and disease category for patients with pulmonary isolates only (B), Denmark, 1991–2022. Patients with samples from both pulmonary and extrapulmonary locations were categorized as having disseminated disease.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: July 08, 2024
Page updated: August 20, 2024
Page reviewed: August 20, 2024
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.