Autochthonous Human Babesiosis Caused by Babesia venatorum, the Netherlands
Niekie Spoorenberg
1, Clara F. Köhler
1, Evelien Vermeulen
1, Suzanne Jurriaans, Marion Cornelissen, Kristina E.M. Persson, Iris van Doorn, Hein Sprong, Joppe W. Hovius, and Rens Zonneveld

Author affiliations: Amsterdam University Medical Center, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, the Netherlands (N. Spoorenberg, E. Vermeulen, S. Jurriaans, M. Cornelissen, I. van Doorn, J.W. Hovius, R. Zonneveld); Amsterdam Institute for Immunology & Infectious Diseases, Amsterdam (N. Spoorenberg, S. Jurriaans, M. Cornelissen, J.W. Hovius, R. Zonneveld); Centre for Infectious Disease Control, National Institute for Public Health and the Environment (RIVM), Bilthoven, the Netherlands (C.F. Köhler, H. Sprong); Lund University, Lund, Sweden (K.E.M. Persson); Skåne University Hospital, Lund (K.E.M. Persson)
Main Article
Figure 3
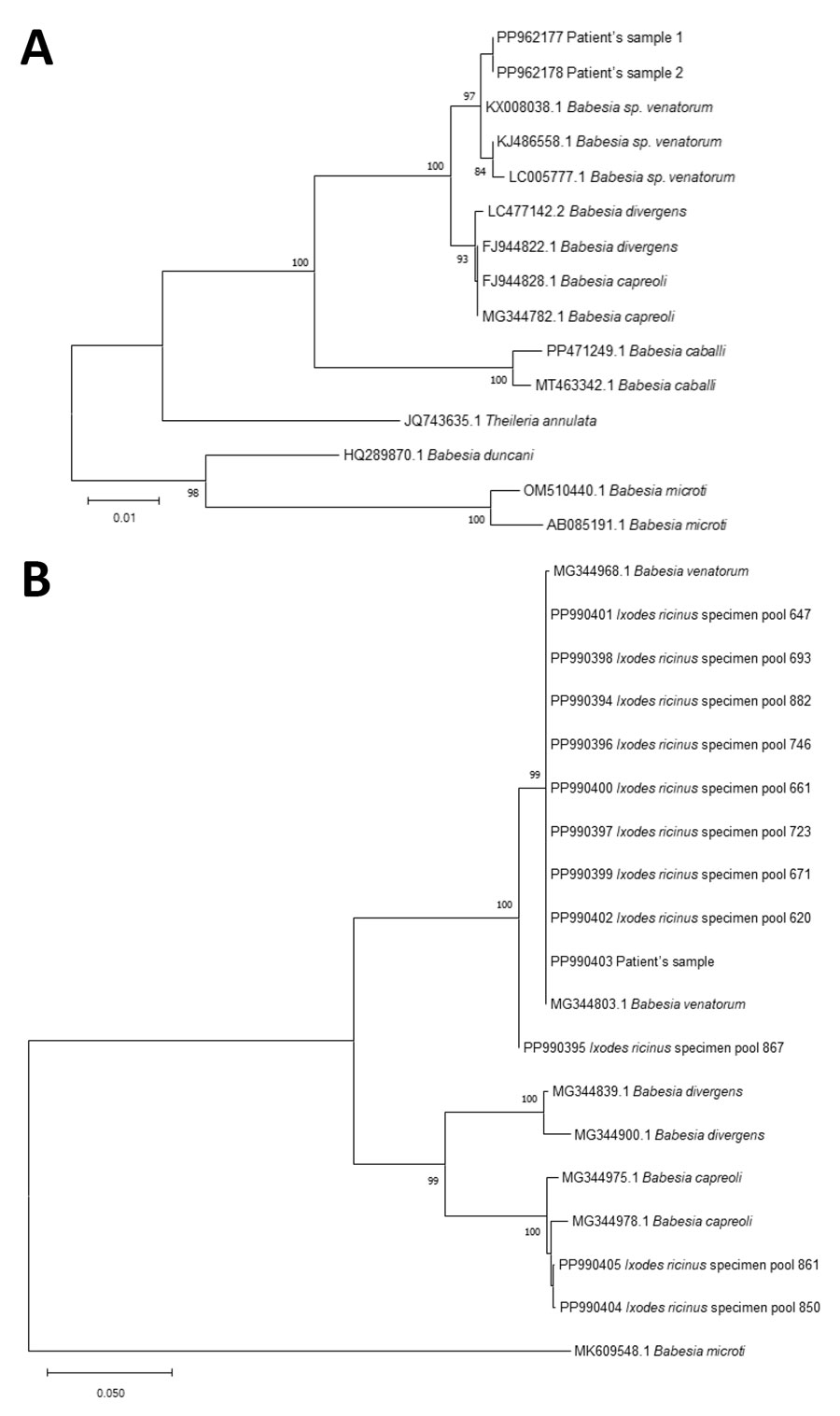
Figure 3. Phylogenetic analysis of Babesia sequences obtained from patient samples in study of autochthonous human babesiosis caused by Babesia venatorum, the Netherlands. A) Neighbor-joining tree of the phylogenetic relationship of Babesia species based on sequences of a fragment of 18S ribosomal RNA. B) Babesia sequences isolated from Ixodes ricinus ticks collected near the patient’s residence (Ixodes ricinus specimen pool 620, 647, 661, 671, 693, 723, 746, 850, 861, 867, and 882), of a fragment of cytochrome oxidase subunit 1. The distance between sequences was calculated using the Kimura 2-parameter model. The bootstrap test was performed with 500 replicates. Bootstrap values >70 are displayed. GenBank accession numbers are provided for all sequences.
Main Article
Page created: August 01, 2024
Page updated: August 21, 2024
Page reviewed: August 21, 2024
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
