Ongoing Evolution of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus, Saudi Arabia, 2023–2024
Ahmed M. Hassan
1, Barbara Mühlemann
1, Tagreed L. Al-Subhi, Jordi Rodon, Sherif A. El-Kafrawy, Ziad Memish, Julia Melchert, Tobias Bleicker, Tiina Mauno, Stanley Perlman, Alimuddin Zumla, Terry C. Jones, Marcel A. Müller, Victor M. Corman, Christian Drosten
2
, and Esam I. Azhar
2
Author affiliation: King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia (A.M. Hassan, T.L. Al-Subhi, S.A. El-Kafrawy, E.I. Azhar); Charité–Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany (B. Mühlemann, J. Rodon, J. Melchert, T. Bleicker, T. Mauno, T.C. Jones, M.A. Müller, V.M. Corman, C. Drosten); German Center for Infection Research, Berlin (B. Mühlemann, J. Melchert, V.M. Corman, C. Drosten); Ministry of Health and Al-Faisal University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia (Z. Memish); Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia, USA (Z. Memish); University of Iowa, Iowa City, Iowa, USA (S. Perlman); University College London, London, UK (A. Zumla); University College London Hospitals Biomedical Research Centre, London (A. Zumla); University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK (T.C. Jones)
Main Article
Figure 1
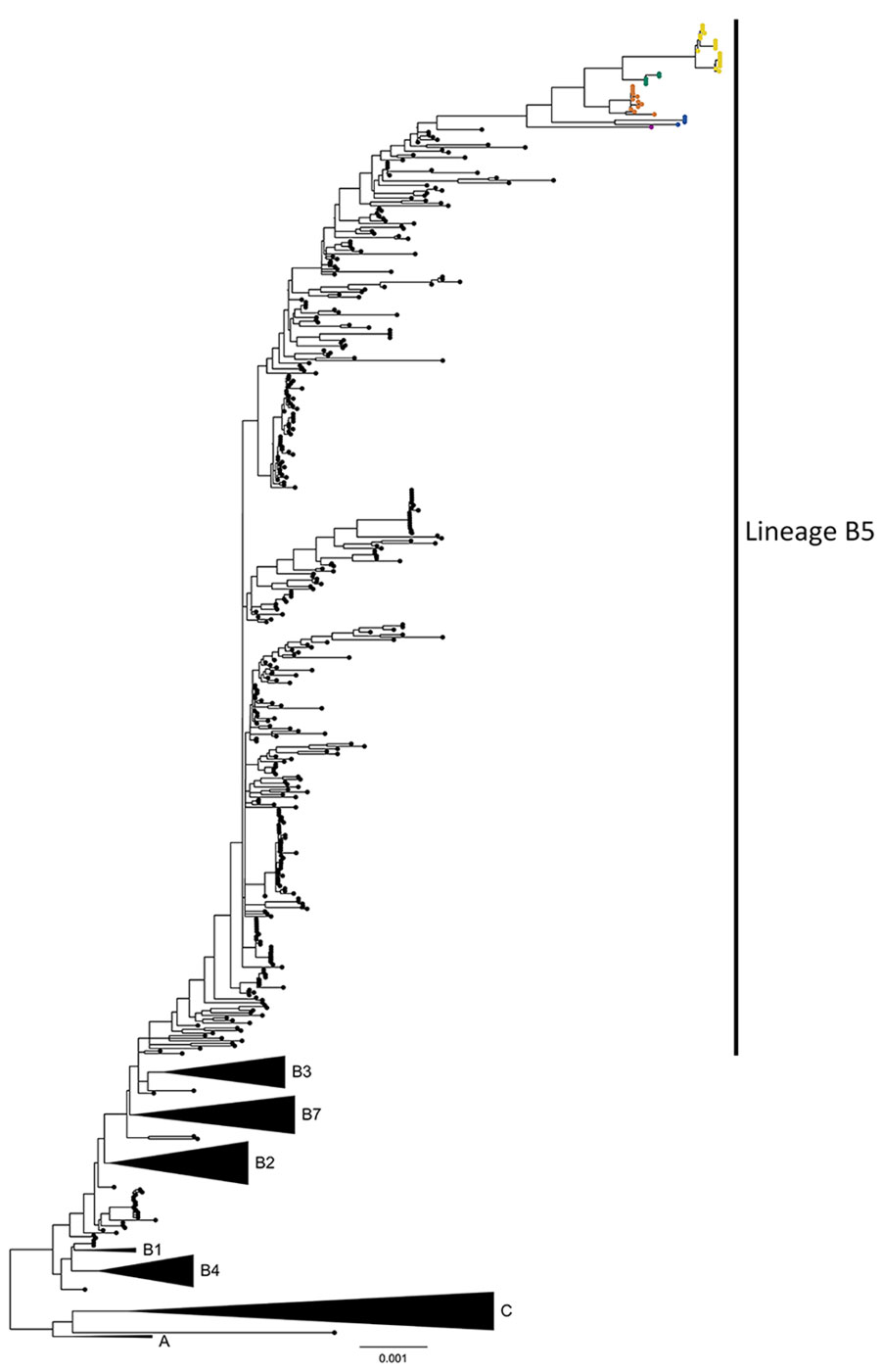
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analysis of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) clades and sample distribution in study of ongoing evolution of virus, Saudi Arabia, 2023–2024. Tree was constructed by using the maximum-likelihood method. Black circles indicate 620 complete MERS-CoV genomes sampled until 2019; colored circles indicate 41 MERS-CoV genomes sequenced in this study. Blue circles indicate B5-2023.1, orange circles B5-2023.2, green circles B5-2023.3, yellow circles B5-2023.4, and magenta B5-2023.5 sublineages. Black triangles indicate collapsed clades A, C, B1–B4, and B7. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
Main Article
Page created: October 30, 2024
Page updated: December 22, 2024
Page reviewed: December 22, 2024
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
