Volume 31, Supplement—May 2025
SUPPLEMENT ISSUE
Supplement
Genomic Characterization of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Associated with Multiple Sources, United States
Figure 1
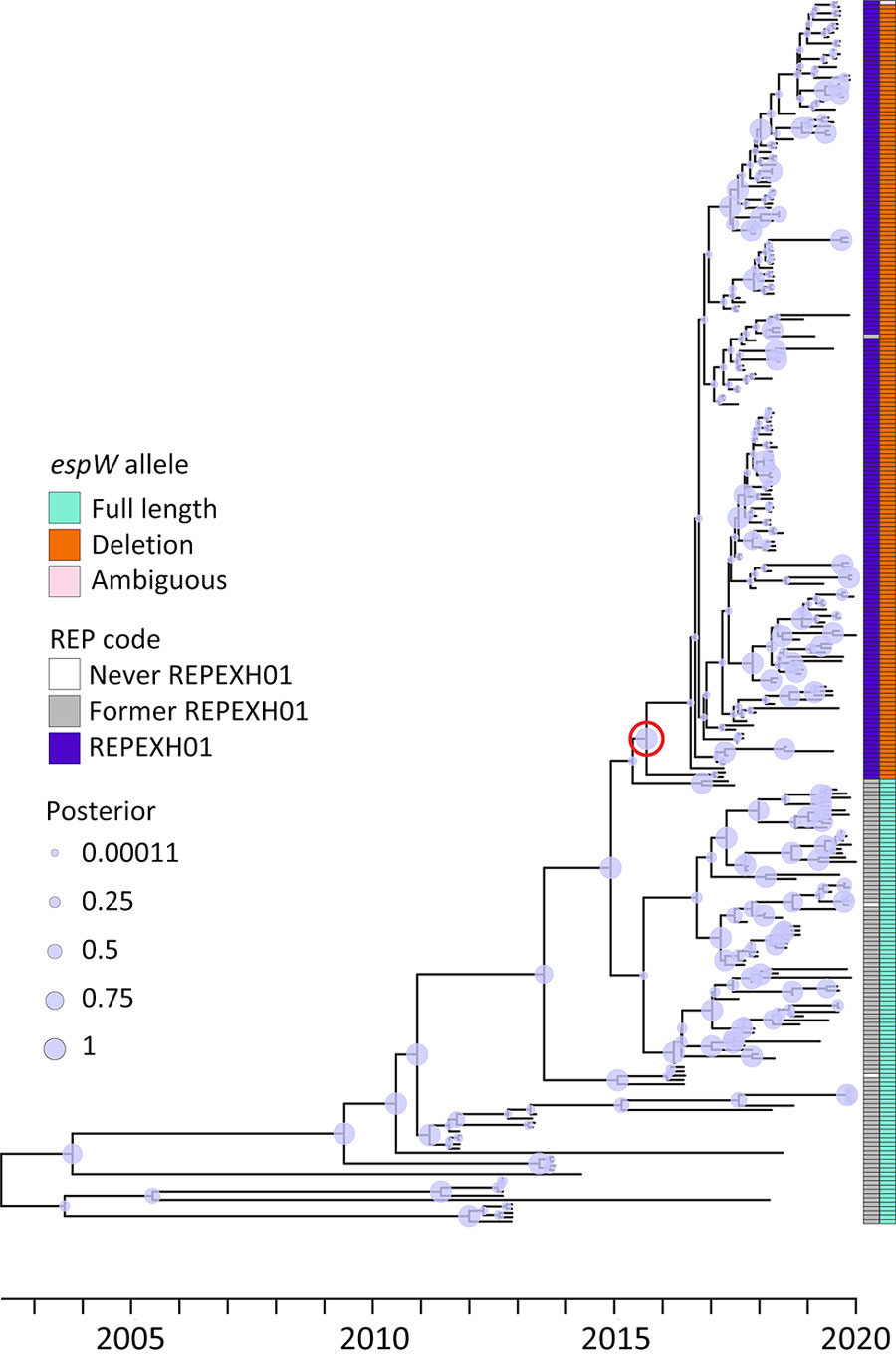
Figure 1. Time-calibrated tree for 286 former and current REPEXH01 isolates with associated metadata used for genomic characterization of Escherichia coli O157:H7 associated with multiple sources, United States. The tree was constructed using BEAST2 (https://beast.community) on an alignment of high-quality single-nucleotide polymorphisms. The red circle indicates the most common recent ancestor of the REPEXH01 isolates and corresponds to December 2015. On the right side, the first column indicates the current REPEXH01 isolates (purple), former REPEXH01 isolates (gray), or isolates that were never part of the REPEXH01 definition (white). The second column indicates the espW allele: teal indicates the full-length allele, orange indicates the presence of a single base pair deletion; and pink indicates that espW is present but the allele could not be determined due to inadequate sequencing data. Circles on the branches indicate the posterior probability. REP, reocurring, emerging, and persistent; REPHEXH01, recurring strain of Shiga toxin–producing E. coli O157:H7.