Carbapenem-Resistant, Virulence Plasmid–Harboring Klebsiella pneumoniae, United States
Jianping Jiang, Tengfei Long, Adeline R. Porter, Arianne Lovey, Annie Lee, Jesse Thomas Jacob, Cesar A. Arias, Robert Bonomo, Robert Kalayjian, Yanan Zhao, Frank R. DeLeo, David van Duin, Barry N. Kreiswirth

, and Liang Chen

Author affiliation: Hackensack-Meridian Health Center for Discovery and Innovation, Nutley, New Jersey, USA (J. Jiang, T. Long, A. Lovey, A. Lee, Y. Zhao, B.N. Kreiswirth, L. Chen); National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Rocky Mountain Laboratories, Hamilton, Montana, USA (A.R. Porter, F.R. DeLeo); Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia, USA (J.T. Jacob); Houston Methodist Hospital and Houston Methodist Research Institute, Houston, Texas, USA (C.A. Arias); Louis Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center, Cleveland, Ohio, USA (R.A. Bonomo); Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Cleveland (R.A. Bonomo); MetroHealth Medical Center, Cleveland (R. Kalayjian); University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina, USA (D. van Duin)
Main Article
Figure 5
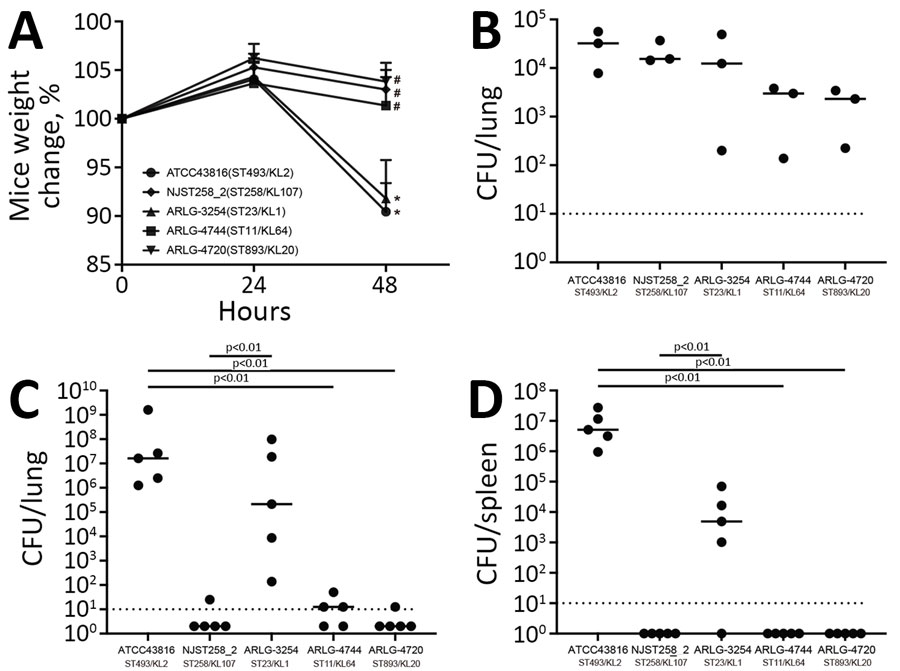
Figure 5. Virulence comparison of 3 selected isolates in study of carbapenem-resistant, virulence plasmid–harboring Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates, United States. Virulence phenotypes were determined in a murine model of K. pneumoniae pneumonia. A) Changes in mouse weight relative to the baseline at 0 h during the course of infection (n = 5). Results represent the mean (dots) + standard deviation (t bars) of the indicated number of samples. Asterisks (*) indicate p<0.05 vs. 24 h; hash marks (#) indicate p<0.05 vs. ATCC43816. B–D) Bacteria recovered from mouse lungs at 2 h (B, n = 3) and 48 h (C, n = 5) postinfection and from spleens at 48 h postinfection (D, n = 5). Individual CFU values (dots) and mean values (horizontal lines) are shown. We used t-tests for all the comparisons. Dashed lines indicate limits of detection. KL, capsular locus; ST, sequence type.
Main Article
Page created: February 18, 2025
Page updated: March 24, 2025
Page reviewed: March 24, 2025
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
