Rapid Transmission and Divergence of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus faecium Sequence Type 80, China
Liqiang Li
1, Xingwei Wang
1, Yanyu Xiao, Bing Fan, Jiehong Wei, Jie Zhou, Zetian Lai, Yanpeng Zhang, Hongmei Mo, Li Zhang, Dixian Luo, Dayong Gu, Shucai Yang, Yidi Wang, Jiuxin Qu

, and
Shenzhen Pathogen Infection Research Alliance (SPIRA)
Author affiliation: Shenzhen Third People’s Hospital Department of Clinical Laboratory; National Clinical Research Center for Infectious Diseases, Second Affiliated Hospital of Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China (L. Li, X. Wang, Y. Xiao, Y. Wang, J. Qu); Shenzhen Institute of Translational Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital, Shenzhen (B. Fan, Y. Zhang, D. Gu); Medical Laboratory of the Third Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen (J. Wei, H. Mo); Pingshan Hospital, Southern Medical University, Pingshan District People’s Hospital of Shenzhen, Shenzhen (J. Zhou, L. Zhang, S. Yang); Shenzhen Nanshan People's Hospital, Shenzhen (Z. Lai, D. Luo); Shenzhen University Medical School, Shenzhen (Z. Lai, D. Luo)
Main Article
Figure 3
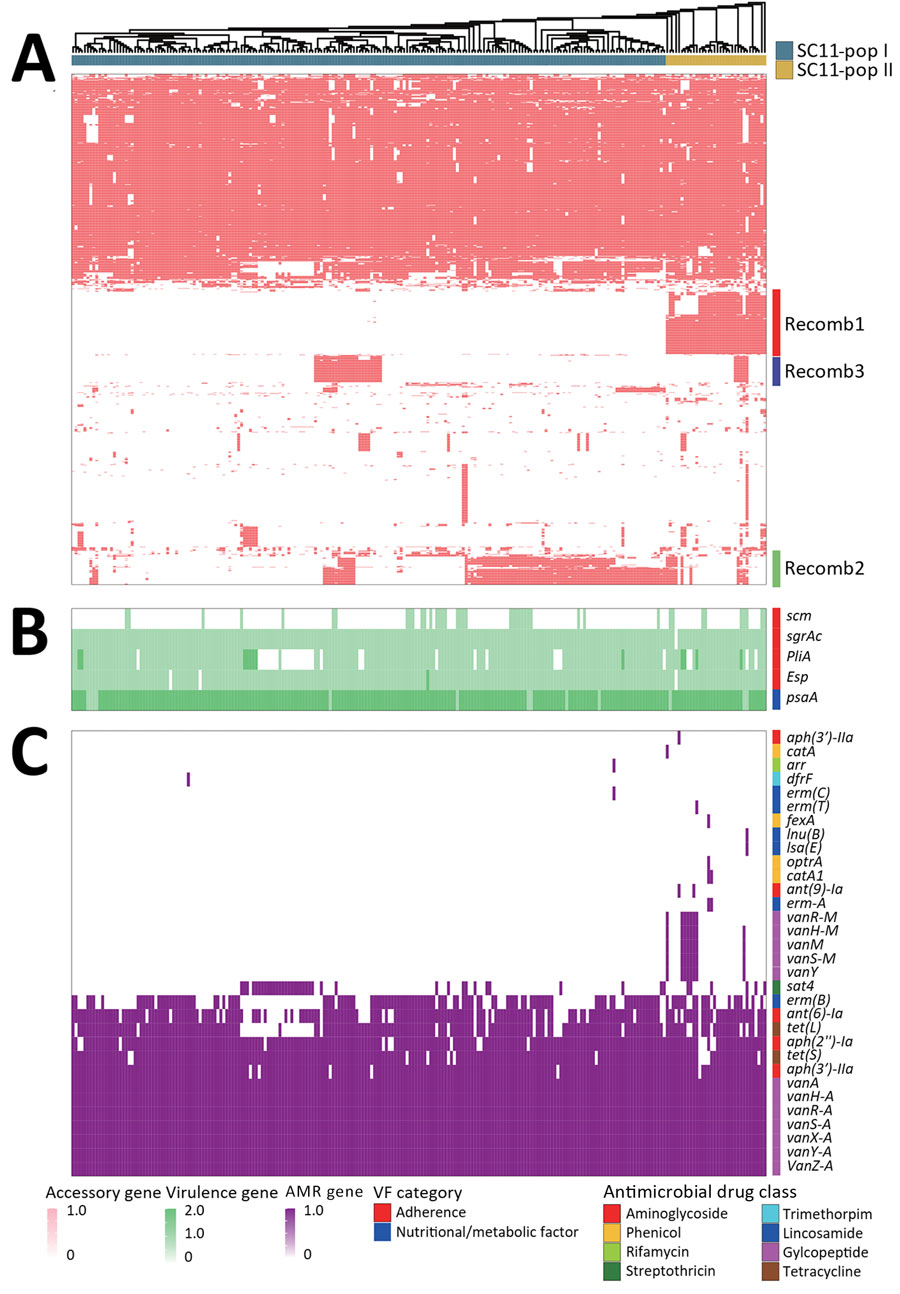
Figure 3. Alignment of SC11 to determine divergence during rapid transmission and divergence of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium ST80, China. To determine the genes associated with the divergence of SC11 we aligned various SC11 genes to pangenomic phylogeny. A) Accessory genes; B) virulence genes; C) AMR genes. Gene copy numbers are displayed in a color grade. We identified 17 total virulence genes; 12 are conserved in all SC11 isolates, and thus only 5 variable virulence genes are shown. Functional categories are indicated by color on the top of the virulence gene heatmap, and drug class corresponding to each AMR gene is shown on the top of AMR gene heatmap. Compared with SC11-pop I, SC11-pop II was more active in acquiring AMR genes against various antibiotic drugs, including sporadic acquisition of aminoglycoside resistance genes ant9Ia and aph3IIIa; rifamycin resistance gene arr; trimethoprim resistance gene dfrF; lincosamide resistance genes ermA, ermC, ermT, lnuB, and lsaE; and phenicol resistance genes fexA, optrA, catA1, and catA. AMR, antimicrobial resistance; pop, population; ARG, antimicrobial resistance gene; SC, sequence cluster; ST, sequence type.
Main Article
Page created: March 24, 2025
Page updated: April 25, 2025
Page reviewed: April 25, 2025
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
