Volume 31, Number 8—August 2025
CME ACTIVITY - Research
Scheffersomyces spartinae Fungemia among Pediatric Patients, Pakistan, 2020–2024
Figure 3
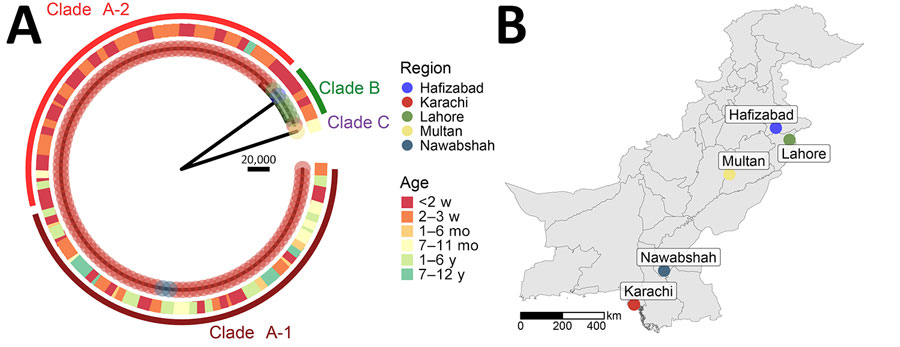
Figure 3. Whole-genome phylogeny and locations of Scheffersomyces spartinae fungemia isolates among pediatric patients, Pakistan, 2020–2024. A) Midpoint-rooted maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree from whole-genome sequence alignment of 108 S. spartinae isolates from human blood cultures. Tip circles indicate the patient’s city of residence. Outer squares indicate the age of the patient. Arcs indicate observed major phylogenetic clades or subclades. Scale bar indicates number of single-nucleotide variant differences corresponding to branch lengths. B) Cities of residence for all patients with S. spartinae–positive blood cultures detected by whole-genome sequencing.
Page created: June 02, 2025
Page updated: July 24, 2025
Page reviewed: July 24, 2025
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.