Volume 31, Number 8—August 2025
Online Report
Optimal Timing for Expanding Diagnostic Laboratories, South Korea
Figure 1
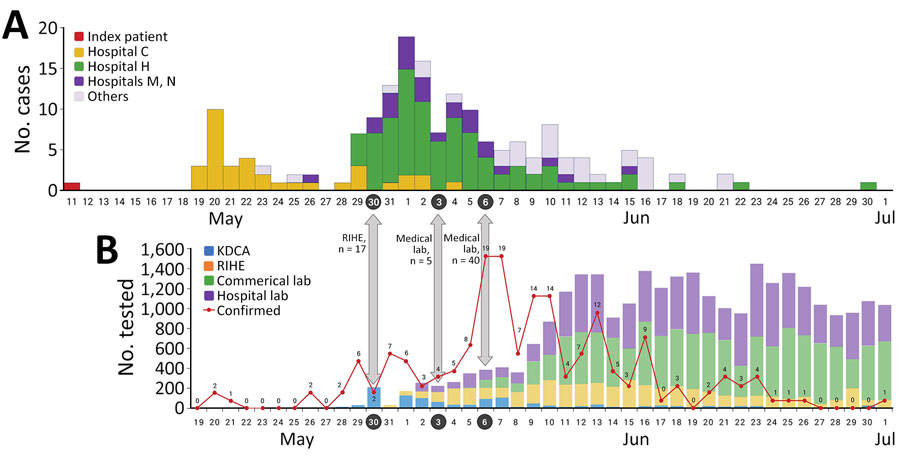
Figure 1. Epidemiologic curve of Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) cases and tests in South Korea during May–July 2015. A) Epidemiologic curve according to date of MERS symptom onset in patients, adapted from KDCA report (4). B) Number of daily tests for MERS, adapted from Ministry of Health and Welfare white paper (5). Gray arrows indicate expansion dates of new testing facilities. Red line with numbers indicates newly positive laboratory results. KDCA, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; lab, laboratory; RIHE, Research Institute of Health and Environment.
References
- Group of Seven, Pandemic Preparedness Partnership. 100 Days Mission to respond to future pandemic threats. Jun 12, 2021 [cited 2023 Oct 11]. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/992762/100_Days_Mission_to_respond_to_future_pandemic_threats__3_.pdf
- Mathieu E, Ritchie H, Rodés-Guirao L, Appel C, Gavrilov D, Giattino C, et al. COVID-19 pandemic [cited 2023 Oct 11]. https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus
- Yang S, Jang J, Park SY, Ahn SH, Kim SS, Park SB, et al. COVID-19 outbreak report from January 20, 2020 to January 19, 2022 in the Republic of Korea. Public Health Wkly Rep. 2022;15:796–805.
- Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus outbreak in the Republic of Korea, 2015. Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2015;6:269–78. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ministry of Health and Welfare. The 2015 MERS outbreak in the Republic of Korea: learning from MERS (in Korean). Jul 29, 2016 [cited 2023 Oct 11]. https://www.mohw.go.kr/board.es?mid=a10411010100&bid=0019&tag=&act=view&list_no=337407
- Park JS, Choi YS, Yoo CK. Emergency use authorization of in-vitro diagnostics for infectious disease. Public Health Wkly Rep. 2017;10:555–9.
- Kim JH, An JAR, Min PK, Bitton A, Gawande AA. How South Korea responded to the Covid-19 outbreak in Daegu. NEJM Catal Innov Care Deliv. 2020;1:. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Sung H, Yoo CK, Han MG, Lee SW, Lee H, Chun S, et al. Preparedness and rapid implementation of external quality assessment helped quickly increase COVID-19 testing capacity in the Republic of Korea. Clin Chem. 2020;66:979–81. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hong KH, Lee SW, Kim TS, Huh HJ, Lee J, Kim SY, et al. Guidelines for laboratory diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Korea. Ann Lab Med. 2020;40:351–60. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hong KH, Kim GJ, Roh KH, Sung H, Lee J, Kim SY, et al.; COVID-19 Task Force, the Korean Society for Laboratory Medicine and the Bureau of Infectious Disease Diagnosis Control, the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. Update of guidelines for laboratory diagnosis of COVID-19 in Korea. Ann Lab Med. 2022;42:391–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sung H, Roh KH, Hong KH, Seong MW, Ryoo N, Kim HS, et al. COVID-19 molecular testing in Korea: practical essentials and answers from experts based on experiences of emergency use authorization assays. Ann Lab Med. 2020;40:439–47. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: June 23, 2025
Page updated: July 22, 2025
Page reviewed: July 22, 2025
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.