Volume 31, Number 8—August 2025
Research
Transmission Dynamics of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) and A(H5N6) Viruses in Wild Birds, South Korea, 2023–2024
Figure 4
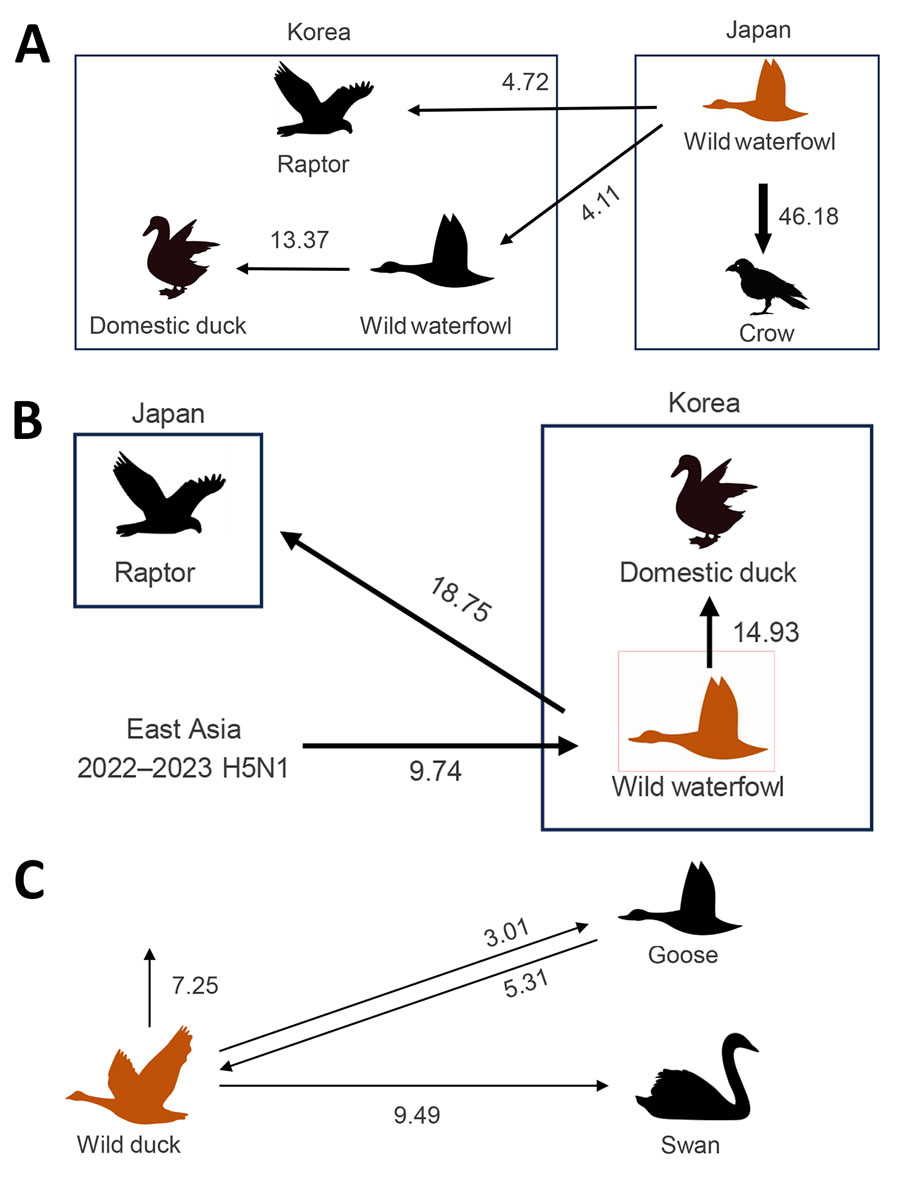
Figure 4. Transmission dynamics of highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) A(H5N1) and A(H5N6) viruses in wild birds, South Korea and Asia, 2023–2024. A, B) Transmission dynamics inferred using the hemagglutinin gene of H5N1 (A) and H5N6 (B) viruses, incorporating the host trait. C) Transmission dynamics inferred using the hemagglutinin genes of both HPAI H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b and H5N6 viruses. Arrows represent the direction of the viral transmission; annotated values represent Bayes factors. Thick arrow indicates a strongly supported route (Bayes factor >20, posterior probability >0.8). Orange indicates the largest source trait.
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: June 23, 2025
Page updated: July 21, 2025
Page reviewed: July 21, 2025
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.