Volume 6, Number 3—June 2000
Research
Rhinosporidium seeberi: A Human Pathogen from a Novel Group of Aquatic Protistan Parasites
Figure 2
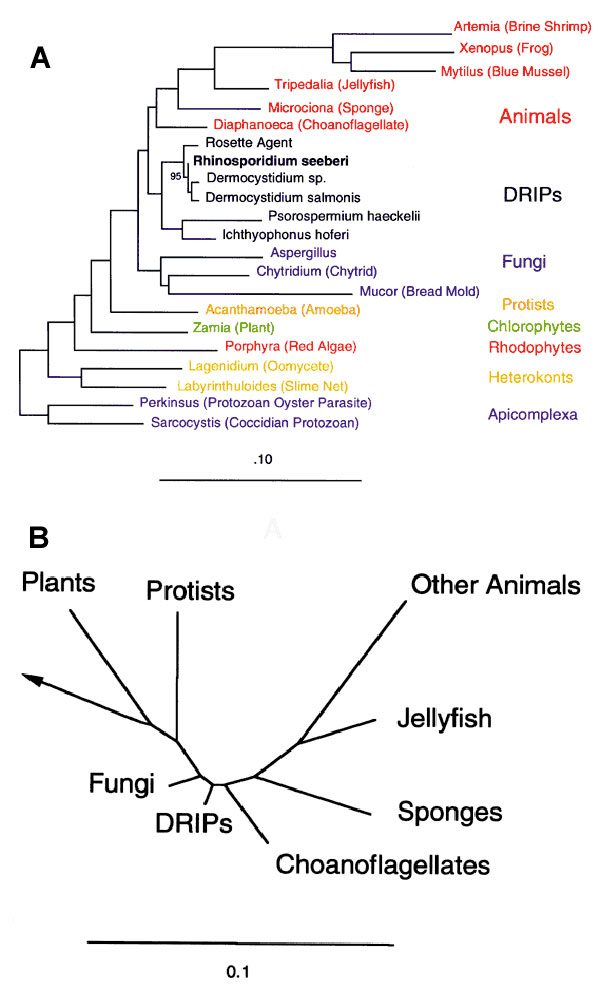
Figure 2. Phylogeny of Rhinosporidium seeberi and the DRIPs clade of protists (Ichthyosporea). A. Phylogenetic tree inferred from the 18S rDNA sequences of R. seeberi and other selected eukaryotes by using a maximum likelihood algorithm; 1,350 masked positions were used for analysis. Bootstrap values were generated from 100 resamplings. The bar, which represents 0.1 base changes per nucleotide position, is a measure of evolutionary distance. B. Phylogenetic tree using the data from A, but with pruning and grouping to show the broader evolutionary position of the DRIPs clade.
Page created: December 16, 2010
Page updated: December 16, 2010
Page reviewed: December 16, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.