Volume 7, Number 1—February 2001
Synopsis
Quinolone and Macrolide Resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli: Resistance Mechanisms and Trends in Human Isolates
Figure 2
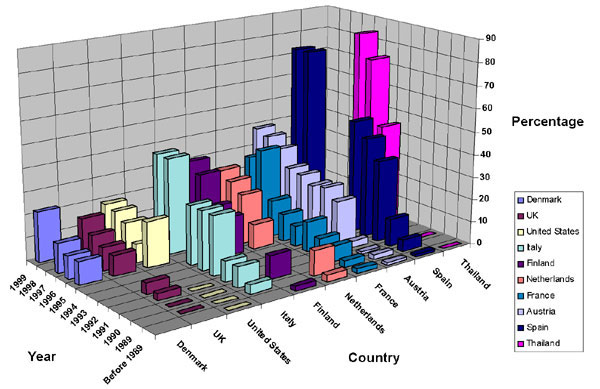
Figure 2. Trends for quinolone resistance rates (in percentages) among Campylobacter coli and C. jejuni combined from human sources around the world. The bars represent both nalidixic acid and fluoroquinolone resistance and are based on mean values of resistance from numerous reports (9,17,24,27,39,43,56-58,61-64,72-75,78,88, plus pers. comm. from Feirel G and Rautelin H, and unpub. data from Nachamkin I.).
References
- Tauxe RV. Nachamkin I, Blaser MJ, Tompkins LS, editors. Campylobacter jejuni: current status and future trends. Washington: American Society for Microbiology; 1992. p. 9-19.
- Blaser MJ, Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R, eds. Principles and practice of infectious diseases. 4th ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone Inc.;1995. p. 1948-56.
- Allos BM, Blaser MJ. Campylobacter jejuni and the expanding spectrum of related infections. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;20:1092–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dryden MS, Gabb RJ, Wright SK. Empirical treatment of severe acute community-acquired gastroenteritis with ciprofloxacin. Clin Infect Dis. 1996;22:1019–25.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Skirrow MB, Blaser MJ. Blaser MJ, Smith PD, Ravdin JI, Greenberg HB et al., editors. Infections of gastrointestinal tract. New York: Raven Press; 1995. p. 825-48.
- Wistrom J, Norrby SR. Fluoroquinolones and bacterial enteritis, when and for whom? J Antimicrob Chemother. 1995;36:23–39. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Piddock LJ. Quinolone resistance and Campylobacter spp. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1995;36:891–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Adler-Mosca H, Lüthy-Hottenstein J, Martinetti Lucchini G, Burnens A, Altwegg M. Development of resistance to quinolones in five patients with campylobacteriosis treated with norfloxacin or ciprofloxacin. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991;10:953–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Endtz HP, Ruijs GJ, van Klingeren B, Jansen WH, van der Reyden T, Mouton RP. Quinolone resistance in Campylobacter isolated from man and poultry following the introduction of fluoroquinolones in veterinary medicine. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991;27:199–208. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Smith KE, Besser JM, Hedberg CW, Leano FT, Bender JB, Wicklund JH, Quinolone-resistant Campylobacter jejuni infections in Minnesota, 1992-1998. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:1525–32. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Prescott JF, Baggot JD. Antimicrobial therapy in veterinary medicine. 2nd ed. Ames (IA): Iowa State University Press; 1993.
- Taylor DE. In: Nachamkin I, Blaser MJ, Tompkins LS, editors. Campylobacter jejuni - current status and future trends. Washington: American Society for Microbiology; 1992. p. 74-86.
- Yan W, Taylor DE. Characterization of erythromycin resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991;35:1989–96.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Taylor DE, Ge Z, Purych D, Lo T, Hiratsuka K. Cloning and sequence analysis of two copies of a 23S rRNA gene from Helicobacter pylori and association of clarithromycin resistance with 23S rRNA mutations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1997;41:2621–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Trieber CA, Taylor DE. In: Mobley HLT, Nachamkin I, McGee D, editors. Abstracts and final program of the 10th International Workshop on Campylobacter, Helicobacter and Rlated Oganisms. Baltimore: University of Maryland School of Medicine; 1999; Abstract CA6. p. 3.
- Wang Y, Huang WM, Taylor DE. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the Campylobacter jejuni gyrA gene and characterization of quinolone resistance mutations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993;37:457–63.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ruiz J, Goni P, Marco F, Gallardo F, Mirelis B, Jimenez De Anta T, Increased resistance to quinolones in Campylobacter jejuni: a genetic analysis of gyrA gene mutations in quinolone-resistant clinical isolates. Microbiol Immunol. 1998;42:223–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gibreel A, Sjögren E, Kaijser B, Wretlind B, Sköld O. Rapid emergence of high-level resistance to quinolones in Campylobacter jejuni associated with mutational changes in gyrA and parC. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998;42:3276–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gootz TD, Martin BA. Characterization of high-level quinolone resistance in Campylobacter jejuni. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991;35:840–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Charvalos E, Tselentis Y, Hamzehpour MM, Köhler T, Pechere J-C. Evidence for an efflux pump im multidrug-resistant Campylobacter jejuni. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995;39:2019–22.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- van Diest J, de Jong A. Overview of quinolone usage for food-producing animals. In: Use of quinolones in food animals and potential impact on human health. Report and proceedings of a WHO meeting. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1999. p.97.
- Antibiotic resistance in the European Union associated with therapeutic use of veterinary medicines. Report and qualitative risk assessment by the committee for veterinary medical products. London: The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medical Products; 1999.
- Jacobs Reitsma WF, Kan CA, Bolder NM. The induction of quinolone resistance in Campylobacter in broilers by quinolone treatment. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1994; 19228–31.
- Aarestrup FM, Nielsen EM, Madsen M, Engberg J. Antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of thermophilic Campylobacter spp. from humans, pigs, cattle, and broilers in Denmark. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1997;41:2244–50.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bager F, ed. Danmap 98 - Consumption of antimicrobial agents and occurrence of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria from food animals, food and humans in Denmark. Copenhagen, Denmark: Danish Zoonosis Centre; 1999. p.3.
- Cabrita J, Rodriguez J, Braganca F, Morgado C, Pires I, Penha Goncalves A. Prevalence, biotypes, plasmid profile and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter isolates from wild and domestic animals from Northeast Portugal. J Appl Microbiol. 1992;73:279–85. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Saenz Y, Zarazaga M, Lantero M, Gastanares MJ, Baquero F, Torres C. Antibiotic resistance in Campylobacter strains isolated from animals: Foods, and humans in Spain in 1997-1998. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000;44:267–71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Moore JE, Madden RH, Kerr JR, Wilson TS, Murphy PG. Erythromycin-resistant thermophilic Campylobacter species isolated from pigs [see comments]. Vet Rec. 1996;138:306–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nielsen EM, Nielsen NL. Serotypes and typability of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolated from poultry products. Int J Food Microbiol. 1999;46:199–205. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Endtz HP, Mouton RP, van der Reyden T, Ruijs GJ, Biever M, van Klingeren B. Fluoroquinolone resistance in Campylobacter spp. isolated from human stools and poultry products [letter] [see comments]. Lancet. 1990;335:787. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Li CC, Chiu CH, Wu JL, Huang YC, Lin TY. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of Campylobacter jejuni and coli by using E-test in Taiwan. Scand J Infect Dis. 1998;30:39–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gaunt PN, Piddock LJ. Ciprofloxacin resistant Campylobacter spp. in humans: an epidemiological and laboratory study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1996;37:47–57. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Skirrow MB, Blaser MJ. Nachamkin I, Blaser MJ, Tompkins LS, editors. Campylobacter jejuni: current status and future trends. Washington: American Society for Microbiology; 1992. p. 3-8.
- Neimann J, Engberg J, Mølbak K, Wegener HC. Proceedings of the 4th World Congress on Foodborne Infections and Intoxications. Berlin: Federal Institute for Health Protection of Consumer and Veterinary Medicine; 1998. p. 298-303.
- Engberg J, Gerner-Smidt P, Scheutz F, Nielsen EM, On SLW, Mølbak K. Water-borne Campylobacter jejuni infection in a Danish town - a 6-week continuous source outbreak. Clin Microbiol Infect. 1998;4:648–56. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- On SLW, Nielsen EM, Engberg J, Madsen M. Validity of SmaI-defined genotypes of Campylobacter jejuni examined by SalI, KpnI, and BamHI polymorphisms: evidence of identical clones infecting humans, poultry, and cattle. Epidemiol Infect. 1998;120:231–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nielsen EM, Engberg J, Madsen M. Distribution of serotypes of Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli from Danish patients, poultry, cattle and swine. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1997;19:47–56. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Doyle MP, Jones DM, Nachamkin I, Blaser MJ, Tompkins LS, eds. Campylobacter jejuni - current status and future trends. Washington DC: American Society for Microbiology; 1992. p. 45-8.
- Piddock LJV. Working Paper 20.09. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1998. p. 1-9.
- Gallardo F, Gascon J, Ruiz J, Corachan M, de Anta MTJ, Vila J. Campylobacter jejuni as a cause of traveler's diarrhea: clinical features and antimicrobial susceptibility. J Travel Med. 1998;5:23–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mattila L, Peltola H, Siitonen A, Kyronseppa H, Simula I, Kataja M. Short-term treatment of traveler's diarrhea with norfloxacin: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study during two seasons. Clin Infect Dis. 1993;17:779–82.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Friedman CR, Yang S, Rocourt J, Stamey K, Vugia D, Marcus R, Program and Abstracts of 36th annual meeting of the Infectious Diseases Society of America Denver (CO): The Infectious Diseases Society of America; 1998; Abstract 545 Fr, p. 179.
- Rautelin H, Renkonen OV, Kosunen TU. Emergence of fluoroquinolone resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in subjects from Finland. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991;35:2065–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sjögren E, Kaijser B, Werner M. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolated in Sweden: a 10-year follow-up report. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992;36:2847–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sjögren E, Lindblom GB, Kaijser B. Norfloxacin resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolates from Swedish patients. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1997;40:257–61. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Engberg J, Andersen S, Skov R, Aarestrup FM, Gerner-Smidt P. Comparison of two agar dilution methods and three agar diffusion methods including the E-test for antibiotic susceptibility testing of thermophilic Campylobacter species. Clin Microbiol Infect. 1999;5:580–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Orr KE, Lightfoot NF, Sisson PR, Harkis BA, Tveddle JL, Boyd P, Direct milk excretion of Campylobacter jejuni an a dairy cow causing cases of human enteritis. Epidemiol Infect. 1995; 11415–24.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pearson AD, Greenwood MH, Donaldson J, Healing TD, Jones DM, Shahamat M, Continuous source outbreak of campylobacteriosis traced to chicken. J Food Prot. 2000;63:309–14.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Owen RJ, Leeton S. Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of the flaA gene of Campylobacter jejuni for subtyping human, animal and poultry isolates. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1999;176:345–50. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Funke G, Baumann R, Penner JL, Altwegg M. Development of resistance to macrolide antibiotics in an AIDS patient treated with clarithromycin for Campylobacter jejuni diarrhea. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1994;13:612–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Segreti J, Gootz TD, Goodman LJ, Parkhurst GW, Quinn JP, Martin BA, High-level quinolone resistance in clinical isolates of Campylobacter jejuni. J Infect Dis. 1992;165:667–70.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tee W, Mijch A. Campylobacter jejuni bacteremia in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected and non-HIV-infected patients: comparison of clinical features and review. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;26:91–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ellis-Pegler RB, Hyman LK, Ingram RJ, McCarthy M. A placebo controlled evaluation of lomefloxacin in the treatment of bacterial diarrhoea in the community. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1995;36:259–63. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Molina J, Casin I, Hausfater P, Giretti E, Welker Y, Decazes J, Campylobacter infections in HIV-infected patients: clinical and bacteriological features. AIDS. 1995;9:881–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chatzipanagiotou S, Papavasiliou E, Malamou Lada E. Isolation of Campylobacter jejuni strains resistant to nalidixic acid and fluoroquinolones from children with diarrhea in Athens, Greece [letter]. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1993;12:566–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Reina J, Ros MJ, Serra A. Susceptibilities to 10 antimicrobial agents of 1,220 Campylobacter strains isolated from 1987 to 1993 from feces of pediatric patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994;38:2917–20.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sanchez R, Fernandez Baca V, Diaz MD, Munoz P, Rodriguez Creixems M, Bouza E. Evolution of susceptibilities of Campylobacter spp. to quinolones and macrolides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994;38:1879–82.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Feierl G, Berghold C, Furpass T, Marth E. Further increase in ciprofloxacin-resistant Campylobacter jejuni/coli in Styria, Austria. Clin Microbiol Infect. 1999;5:59–60. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gaudreau C, Gilbert H. Antimicrobial resistance of clinical strains of Campylobacter jejuni subsp. jejuni isolated from 1985 to 1997 in Quebec, Canada. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998;42:2106–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gaudreau C, Gilbert H. Mobley HLT, Nachamkin I, McGee D, editors. Abstracts and final program of the 10th International Workshop on Campylobacter, Helicobacter and Related Organisms. Baltimore: University of Maryland School of Medicine; 1999. Abstract CA3, p. 2.
- Bager F, ed. DANMAP 97 - Consumption of antimicrobial agents and occurrence of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria from food animals, food and humans in Denmark. Copenhagen: Danish Zoonosis Centre; 1998. p.3.
- Bager F, ed. DANMAP 99 - Consumption of antimicrobial agents and occurrence of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria from food animals, food and humans in Denmark. Copenhagen: Danish Zoonosis Centre; 2000.
- Hänninen ML, Pajarre S, Klossner ML, Rautelin H. Typing of human Campylobacter jejuni isolates in Finland by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36:1787–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Megraud F. Les infections à Campylobacter en France (1986-1997). Bulletin Epidémiologique Annuel. 1998;2:83–4.
- Varga J, Fodor L. Biochemical characteristics, serogroup distribution, antibiotic susceptibility and age-related significance of Campylobacter strains causing diarrhoea in humans in Hungary. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1998;288:67–73.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Itoh T, Tadano K, Obata H, Shingaki K, Kai A, Saito K, Emergence of quinolone-resistance in clinical isolates of Campylobacter jejuni in Japan. In: Newell DG, Ketley J, Feldman RA, editors. In: Abstracts of the 8th International Workshop on Campylobacters, Helicobacters and Related Organisms; 1995 Jul 10-13; t Winchester, United Kingdom. New Haw, Addlestone, England: Central Veterinary Laboratory; 1995. p. 83.
- Piersimoni C, Crotti D, Nista D, Bornigia G, de Sio G. Newell DG, et al, editors. Abstracts of the 8th International Workshop on Campylobacters, Helicobacters and Related Organisms; 1995 Jul 10-13; Winchester, United Kingdom. New Haw, Addlestone, England: Central Veterinary Laboratory; 1995; p. 88.
- Crotti D, Medori MC, Fonzo G, Del Sante M, Silvestrini R. Clinical microbiology of Campylobacter enteritis in our experience. Clin Microbiol Infect. 1999;7(Suppl. 3):267.
- Crotti D, Fonzo G, D'Annibale ML, Medori M. C. Luzzi I, Mobley HLT, et al, In: Mobley HLT, Nachamkin I, McGee D, editors. Abstracts and final program of the 10th International Workshop on Campylobacter, Helicobacter and Related Organisms. Baltimore: University of Maryland School of Medicine; 1999. Abstract CA7. p. 4.
- Dowling J, MacCulloch D, Morris AJ. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Campylobacter and Yersinia enterocolitica isolates [letter]. N Z Med J. 1998;111:281.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lim YS, Tay L. A one-year study of enteric Campylobacter infections in Singapore. J Trop Med Hyg. 1992;95:119–23.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Navarro F, Miro E, Mirelis B, Prats G. Campylobacter spp. antibiotic susceptibility [letter; comment]. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1993;32:906–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hoge CW, Gambel JM, Srijan A, Pitarangsi C, Echeverria P. Trends in antibiotic resistance among diarrheal pathogens isolated in Thailand over 15 years. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;26:341–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Murphy GS Jr, Echeverria P, Jackson LR, Arness MK, LeBron C, Pitarangsi C. Ciprofloxacin- and azithromycin-resistant Campylobacter causing traveler's diarrhea in U.S. troops deployed to Thailand in 1994. Clin Infect Dis. 1996;22:868–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Frost JA, Thwaites RT. Drug resistance in C. jejuni, C. coli and C. lari isolated from humans in Wales and North West England during 1997. Working Paper 20.10b. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1998.
- Baker CN. The E-Test and Campylobacter jejuni. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992;15:469–72. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- National Antimicrobial resistance monitoring system NARMS - 1997 annual report revised. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 1998.
- Nachamkin I. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli to ciprofloxacin, erythromycin and tetracycline from 1982 to 1992. Med Microbiol Lett. 1992;2:300–5.
- Hirschl AM, Wolf D, Berger J, Rotter ML. In vitro susceptibility of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolated in Austria to erythromycin and ciprofloxacin. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1990;272:443–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Feierl G, Pschaid A, Sixl B, Marth E. Increase of ciprofloxacin resistance in Campylobacter species in Styria, Austria. Int J Med Microbiol Virol Parasitol Infect Dis. 1994;281:471–4.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Stobberingh E, van den Bogaard A, Mevius D, Endtz H. Examples of in-vitro quinolone resistance prevalence trends in humans and animal isolates of food-borne Salmonella and Campylobacter. Working Paper 20.09. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1998.
- Perez Trallero E, Urbieta M, Lopategui CL, Zigorraga C, Ayestaran I. Antibiotics in veterinary medicine and public health [letter; comment]. Lancet. 1993;342:1371–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Reina J. Resistance to fluoroquinolones in Salmonella non-typhi and Campylobacter spp. [letter; comment]. Lancet. 1992;340:1035–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kuschner RA, Trofa AF, Thomas RJ, Hoge CW, Pitarangsi C, Amato S, Use of azithromycin for the treatment of Campylobacter enteritis in travelers to Thailand, an area where ciprofloxacin resistance is prevalent. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;21:536–41.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bowler I, Day D. Emerging quinolone resistance in campylobacters [letter; comment]. Lancet. 1992;340:245. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- McIntyre M, Lyons M. Resistance to ciprofloxacin in Campylobacter spp. [letter; comment]. Lancet. 1993;341:188. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bowler IC, Connor M, Lessing MP, Day D. Quinolone resistance and Campylobacter species [letter]. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1996;38:315. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sam WIC, Lyons MM, Waghorn DJ. Increasing rates of ciprofloxacin resistant Campylobacter [Letter]. J Clin Pathol. 1999;52:709. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shah PM, Schafer V, Knothe H. Medical and veterinary use of antimicrobial agents: implications for public health. A clinician's view on antimicrobial resistance. Vet Microbiol. 1993;35:269–74. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Reina J, Borrell N, Serra A. Emergence of resistance to erythromycin and fluoroquinolones in thermotolerant Campylobacter strains isolated from feces 1987-1991. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992;11:1163–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tee W, Mijch A, Wright E, Yung A. Emergence of multidrug resistance in Campylobacter jejuni isolates from three patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;21:634–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Threlfall EJ, Ward LR, Rowe B. Resistance to ciprofloxacin in non-typhoidal salmonellas from humans in England and Wales - the current situation. Clin Microbiol Infect. 1999;5:130–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mølbak K, Baggesen DL, Aarestrup FM, Ebbesen JM, Engberg J, Frydendahl K, An outbreak of multidrug-resistant, quinolone-resistant Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium DT 104. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1420–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pedersen KB, Aarestrup FM, Jensen NE, Bager F, Jensen LB, Jorsal SE, The need for a veterinary antibiotic policy. Vet Rec 1999;(July 10):50-3.
- Use of quinolones in food animals and potential impact on human health. Report of a WHO meeting, Geneva, Switzerland, 2-5 June 1998. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1998.
Page created: March 16, 2011
Page updated: March 16, 2011
Page reviewed: March 16, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.