Volume 7, Number 3—June 2001
Research
Molecular Epidemiology of Serogroup A Meningitis in Moscow, 1969 to 1997
Figure 3
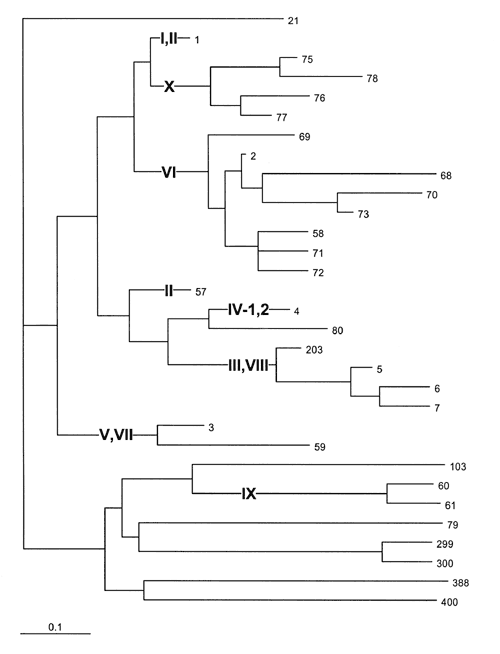
Figure 3. . Midpoint rooted neighbor-joining (NJ) tree of the proportion of seven housekeeping gene fragments that differed between individual sequence types (STs) among 152 serogroup A isolates. The ST designations are indicated at the right of each twig, and the subgroup designations are shown in bold print in the tree. A scale bar showing the distance of 0.1 is at the lower left. STs 1 and 57, containing six subgroup II strains, are widely separated in this tree although they differ only at the pdhC locus (Table 1). These two STs were on adjacent twigs in a UPGMA tree (data not shown), but that tree separated STs 3 and 59 (subgroup V), that differ only at two of the seven loci (Table 1) and are on neighboring twigs in the NJ tree. Given the low number of allelic differences between STs 1 and 57 and STs 3 and 59, their aberrant relative positions in one or the other tree were ignored and their former subgroup assignments have been retained.