Volume 7, Number 5—October 2001
Research
Clonal Expansion of Sequence Type (ST-)5 and Emergence of ST-7 in Serogroup A Meningococci, Africa
Figure
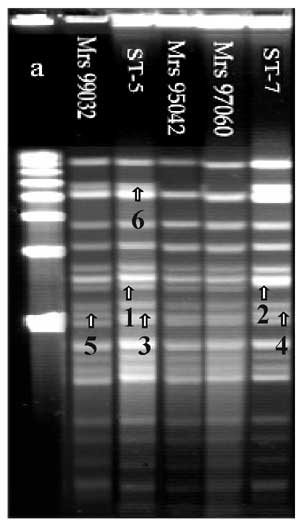
Figure. . Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis analysis of chromosomal DNA (ethidium bromide staining) of 104 strains isolated in Africa. DNA macrorestriction fragments were generated with BglII; 103 out of 104 strains showed closely related profiles. ST-5 pattern was the first pattern found in Africa and the most frequently isolated from 1988 to 1996. The second pattern was the ST-7 pattern, attributable to strains isolated more recently in Algeria, Cameroon, Sudan, Chad, and Niger. ST-7 pattern is closely related to ST-5 pattern but shows four band differences (arrows 1,2,3,4). Mrs 99032, isolated in Dakar in 1999 and belonging to ST-5, showed two band difference with ST-5 pattern (arrows 3,5). Mrs 99066, isolated in Dakar (1999) and belonging to ST 581, showed indistinguishable fingerprint with ST5 pattern (not shown). Strains Mrs 95042 and Mrs 97060, isolated in Burkina Faso in 1995 and in 1997, respectively, and belonging to ST-580, showed one band difference with ST-5 pattern (arrow 6). Lane a, pulsed-field gel electrophoresis marker I (Boehringer Mannheim Biochemicals, Indianapolis, IN).