Volume 9, Number 2—February 2003
Research
Applying Network Theory to Epidemics: Control Measures for Mycoplasma pneumoniae Outbreaks
Table
Notation for epidemiologic interaction network model
| Notation | Definition |
|---|---|
| W | Number of wards in the facility |
| C | Number of caregivers working in the facility |
| μw | Average no. of caregivers working in a ward |
| μc | Average no. of wards in which a caregiver works |
| r | Probability that a given caregiver works in a given ward |
| Ρχ | Probability that a caregiver works in k wards |
| qχ | Probability that a ward has k caregivers working in it |
| ƒ0(x) | Probability generating function (pgf) for the degree distribution of caregivers |
| g0(x) | pgf for the degree distribution of wards |
| ƒ1(x) | First select a random ward, and then select a random caregiver working there. This expression represents the pgf for the number of other wards in which that caregiver works. |
| g1(x) | First select a random caregiver, and then select a random ward associated with that caregiver. This expression represents the pgf for the number of other caregivers working in that ward. |
| τw | Probability of transmission from a ward to a caregiver |
| τc | Probability of transmission from a caregiver to a ward |
| Ф0(x) | pgf for the number of wards affected by transmission from a random caregiver |
| Ф1(x) | First select a random ward and assume that it is affected by the bacterium, then select a random caregiver working there. This expression represents the pgf for the number of other wards affected by that caregiver. |
| Γ0(x) | pgf for the number of caregivers affected by transmission from a random ward |
| Γ1(x) | First select a random caregiver and assume he/she is infected, then select a random ward in which that caregiver works. This expression represents the pgf for the number of other caregivers infected by individuals working/living in that ward. |
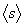 |
Average number of wards affected in an outbreak |
| 1 - Ѕc | The size of the caregiver giant component—the largest set of infected caregivers that are all connected through work in common wards |
| 2-Ѕw | The size of the ward giant component—the largest set of affected wards that are all connected through common caregivers |
| βw(x) | pgf for the number of patients in affected ward w who contract the bacterium |
| Β(x) | pgf for the total number of patients in the facility who are infected during an epidemic |
1We calculate these rates by averaging the fraction of infected patients per ward across the 15 wards and compute the error by taking the standard deviation of these fractions, divided by the square root of the sample size.
Page created: April 20, 2012
Page updated: April 20, 2012
Page reviewed: April 20, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.