Volume 10, Number 4—April 2004
Research
Pneumocystis jiroveci Dihydropteroate Synthase Genotypes in Immunocompetent Infants and Immunosuppressed Adults, Amiens, France
Figure 2
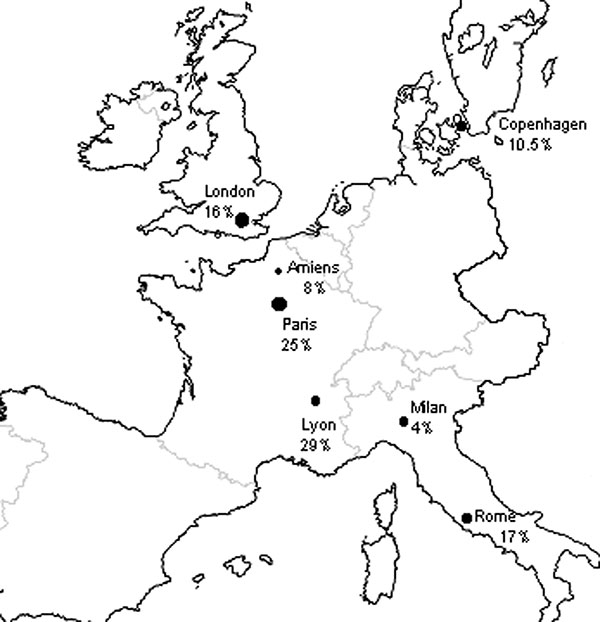
Figure 2. Frequencies of Pneumocystis jiroveci dihydropteroate synthase mutants in patients with Pneumocystis pneumonia and who had no prior sulfonamide exposure, from diverse European cities. Amiens, France (the present study), Paris (13), Lyon (12), Copenhagen (4), Milan, Italy (2), Rome (11), and London (35).
References
- U.S. Public Health Service (USPHS) and Infectious Diseases Society of America. (IDSA). USPHS/IDSA guidelines for the prevention of opportunistic infections in persons infected with human immunodeficiency virus. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1999;48:1–59.
- Ma L, Kovacs JA, Cargnel A, Valerio A, Fantoni G, Atzori C. Mutations in the dihydropteroate synthase gene of human-derived Pneumocystis carinii isolates from Italy are infrequent but correlate with prior sulfa prophylaxis. J Infect Dis. 2002;185:1530–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ma L, Borio L, Masur H, Kovacs JA. Pneumocystis carinii dihydropteroate synthase but not dihydrofolate reductase gene mutations correlate with prior trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or dapsone use. J Infect Dis. 1999;180:1969–78. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Helweg-Larsen J, Benfield TL, Eugen-Olsen J, Lundgren JD, Lundgren B. Effects of mutations in Pneumocystis carinii dihydropteroate synthase gene on outcome of AIDS-associated P. carinii pneumonia. Lancet. 1999;354:1347–51. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Diop Santos L, Lacube P, Latouche S, Kac G, Mayaud C, Marteau M, Contribution of dihydropteroate synthase gene typing for Pneumocystis carinii f.sp. hominis epidemiology. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 1999;46(Suppl):S133–4.
- Kazanjian P, Armstrong W, Hossler PA, Burman W, Richardson J, Lee CH, Pneumocystis carinii mutations are associated with duration of sulfa or sulfone prophylaxis exposure in AIDS patients. J Infect Dis. 2000;182:551–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kazanjian P, Locke AB, Hossler PA, Lane BR, Bartlett MS, Smith JW, Pneumocystis carinii mutations associated with sulfa and sulfone prophylaxis failures in AIDS patients. AIDS. 1998;12:873–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Huang L, Beard CB, Creasman J, Levy D, Duchin JS, Lee S, Sulfa or sulfone prophylaxis and geographic region predict mutations in the Pneumocystis carinii dihydropteroate synthase gene. J Infect Dis. 2000;182:1192–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Armstrong W, Meshnick S, Kazanjian P. Pneumocystis carinii mutations associated with sulfa and sulfone prophylaxis failures in immunocompromised patients. Microbes Infect. 2000;2:61–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mei Q, Gurunathan S, Masur H, Kovacs JA. Failure of co-trimoxazole in Pneumocystis carinii infection and mutations in dihydropteroate synthase gene. Lancet. 1998;351:1631–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Visconti E, Ortona E, Mencarini P, Margutti P, Marinaci S, Zolfo M, Mutations in dihydropteroate synthase gene of Pneumocystis carinii in HIV patients with Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2001;18:547–51. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nahimana A, Rabodonirina M, Zannetti G, Meneau I, Franciolo P, Bille J, Association between a specific Pneumocystis jiroveci dihydropteroate synthase mutation and failure of pyrimethamine/sulfadoxine prophylaxis in HIV-positive and -negative patients. J Infect Dis. 2003;188:1017–23. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Latouche S, Lacube P, Maury E, Bolognini J, Develoux M, Girard PM, Pneumocystis jirovecii dihydropteroate synthase genotypes in French patients with pneumocystosis: a 1998–2001 prospective study. Med Mycol. 2003;41:533–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lane BR, Ast JC, Hossler PA, Mindell DP, Bartlett MS, Smith JW, Dihydropteroate synthase polymorphisms in Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1997;175:482–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Beard CB, Carter JL, Keely SP, Huang L, Pieniazek NJ, Moura IN, Genetic variation in Pneumocystis carinii isolates from different geographic regions: implications for transmission. Emerg Infect Dis. 2000;6:265–72. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Huang L, Friedly J, Morris AM, Carter JL, Turner JR, Merrifield C, Pneumocystis carinii dihydropteroate synthase genotypes in HIV-infected persons residing in San Francisco: possible implications for disease transmission. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2001;48:137–8S. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nevez G, Totet A, Pautard JC, Raccurt C. Pneumocystis carinii detection using nested-PCR in nasopharyngeal aspirates of immunocompetent infants with bronchiolitis. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2001;48(Suppl):S122–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vargas SL, Hughes WT, Santolaya ME, Ulloa AV, Ponce CA, Cabrera CE, Search for primary infection by Pneumocystis carinii in a cohort of normal, healthy infants. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:855–61. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Totet A, Pautard JC, Raccurt C, Roux P, Nevez G. Genotypes at the internal transcribed spacers of the nuclear rRNA operon of Pneumocystis jiroveci in nonimmunosuppressed infants without severe pneumonia. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41:1173–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Totet A, Latouche S, Lacube P, Pautard JC, Jounieaux V, Roux P, Pneumocystis carinii dihydropteroate synthase genotypes in immunocompetent infants and immunosuppressed adults from the same French geographic region. [Suppl]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;▪▪▪:165.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Demanche C, Berthelemy M, Petit T, Polack B, Wakefield AE, Dei-Cas E, Phylogeny of Pneumocystis carinii from 18 primate species confirms host specificity and suggests coevolution. J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39:2126–33. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Navin TR, Beard CB, Huang L, del Rio C, Lee S, Pieniazek NJ, Effect of mutations in Pneumocystis carinii dihydropteroate synthase gene on outcome of P. carinii pneumonia in patients with HIV-1: a prospective study. Lancet. 2001;358:545–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Takahashi T, Hosoya N, Endo T, Nakamura T, Sakashita HK, Imura K, Relationship between mutations in dihydropteroate synthase of Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. hominis isolates in Japan and resistance to sulfonamide therapy. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38:3161–4.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wakefield AE, Lindley AR, Ambrose HE, Denis MC, Miller RF. Limited asymptomatic carriage of Pneumocystis jiroveci in human immunodeficiency virus–infected patients. J Infect Dis. 2003;187:901–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Volpe F, Dyer M, Scaife JG, Darby G, Stammers DK, Delves CJ. The multifunctional folic acid synthesis fas gene of Pneumocystis carinii appears to encode dihydropteroate synthase and hydroxymethyldihydropterin pyrophosphokinase. Gene. 1992;112:213–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ma L, Kovacs JA. Rapid detection of mutations in the human-derived Pneumocystis carinii dihydropteroate synthase gene associated with sulfa resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001;45:776–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Helweg-Larsen J, Eugen-Olsen J, Lundgren B. Rapid detection of dihydropteroate polymorphism in AIDS-related Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia by restriction fragment length polymorphism. Scand J Infect Dis. 2000;32:481–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Huang L, Morris AM, Beard CB. Pneumocystis carinii dihydropteroate synthase mutations and treatment with sulfa or sulfone regimens: a proposal for standardized definitions for clinical evaluation. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2001;48(Suppl):S180–1. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dumoulin A, Mazars E, Seguy N, Gargallo-Viola D, Vargas S, Cailliez JC, Transmission of Pneumocystis carinii disease from immunocompetent contacts of infected hosts to susceptible hosts. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2000;19:671–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Helweg-Larsen J, Tsolaki AG, Miller RF, Lundgren B, Wakefield AE. Clusters of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: analysis of person-to-person transmission by genotyping. Q J Med. 1998;91:813–20.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Miller RF, Ambrose HE, Novelli V, Wakefield AE. Probable mother-to-infant transmission of Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. hominis infection. J Clin Microbiol. 2002;40:1555–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Durand-Joly I, Aliouat el M, Recourt C, Guyot K, Francois N, Wauquier M, et al. Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. hominis is not infectious for SCID mice. J Clin Microbiol. 2002;40:1862–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Institut de veille sanitaire. Surveillance du SIDA en France. Bulletin Epidémiologique Hebdomadaire. 2002;27:133–8.
- Miller RF, Lindley AR, Ambrose HE, Malin AS, Wakefield AE. Genotypes of Pneumocystis jiroveci isolates obtained in Harare, Zimbawe, and London, United Kingdom. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003;47:3979–81. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Beard CB, Fox MR, Hanzlick RL, Guarner J, Carter JL, Del Rio C, Independent transmission cycles for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in immunocompetent infants and in adults with AIDS. In: Abstracts of the VII International Worskhops on Opportunistic Protists; Cincinnati, Ohio; 2001 June 13–16; Abstract PL94.
- Nevez G, Raccurt C, Vincent P, Jounieaux V, Dei-Cas E. Pulmonary colonization with Pneumocystis carinii in human immunodeficiency virus–negative patients: assessing risk with blood CD4+ T cell counts. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;29:1331–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Armbruster C, Hassl A, Kriwanek S. Pneumocystis carinii colonization in the absence of immunosuppression. Scand J Infect Dis. 1997;29:591–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sing A, Roggenkamp A, Autenrieth IB, Heesemann J. Pneumocystis carinii carriage in immunocompetent patients with primary pulmonary disorders as detected by single or nested PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 1999;37:3409–10.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Miller RF, Ambrose HE, Wakefield AE. Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. hominis DNA in immunocompetent health care workers in contact with patients with P. carinii pneumonia. J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39:3877–82. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: February 09, 2011
Page updated: February 09, 2011
Page reviewed: February 09, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.