Volume 14, Number 11—November 2008
Dispatch
Phylogenetics and Pathogenesis of Early Avian Influenza Viruses (H5N1), Nigeria
Figure
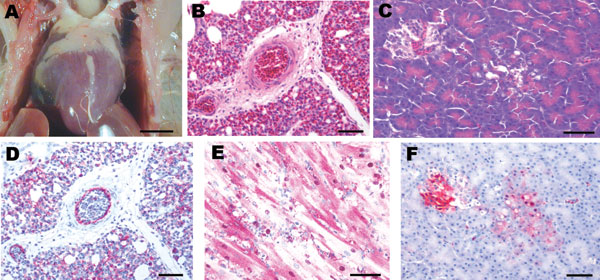
Figure. Experimental studies in chickens inoculated intranasally with highly pathogenic influenza A/chicken/Nigeria/228-5/2005 (H5N1) and sampled 2 days postinoculation. A) Photograph (scale bar = 1 cm) of a gross lesion, showing petechia in epicardial fat in the coronary groove. B,C) Photomicrographs (scale bars = 50 μm) of tissue sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin, showing severe histiocytic and heterophilic interstitial pneumonia with moderately interlobular edema (panel B) and pancreatic acinar epithelium (panel C). D–F) Photomicrographs (scale bars = 50 μm) of tissue sections stained immunohistochemically to demonstrate avian influenza virus nucleoprotein, showing avian influenza virus antigen in pulmonary and blood vessel endothelial cells and histiocytes (panel D), nuclei and cytoplasm of cardiac myocytes (panel E), and pancreatic acinar epithelium and islet cells (panel F).