Volume 15, Number 10—October 2009
Dispatch
Novel Rickettsia in Ticks, Tasmania, Australia
Figure 2
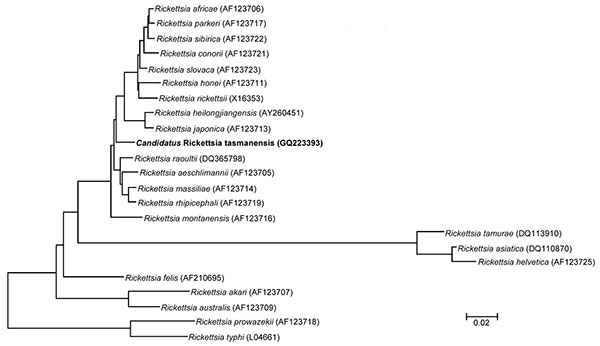
Figure 2. Phylogenetic tree showing the relationship of a 4,834-bp fragment of the outer membrane protein B gene of Candidatus Rickettsia tasmanensis (in boldface) among all validated rickettsia species. The tree was prepared by using the neighbor-joining algorithm within the MEGA 4 software (10). Bootstrap values are indicated at each node. Scale bar indicates 2% nucleotide divergence.
References
- Unsworth NB, Stenos J, Graves SR, Faa AG, Cox GE, Dyer JR, Flinders Island spotted fever rickettsioses caused by “marmionii” strain Rickettsia honei, eastern Australia. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:566–73. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chin RH, Jennens ID. Rickettsial spotted fever in Tasmania. Med J Aust. 1995;162:669.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Watts MR, Benn RA, Hudson BJ, Graves S. A case of prolonged fatigue following an acute rickettsial infection. QJM. 2008;101:591–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sexton DJ, Dwyer B, Kemp R, Graves S. Spotted fever group rickettsial infections in Australia. Rev Infect Dis. 1991;13:876–86.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Roberts FH. Australian ticks. Melbourne: Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation; 1970.
- Parker R, Kohls G, Cox G, Davis G. Observations on an infectious agent from Amblyomma maculatum. Public Health Rep. 1939;54:1482–4.
- Paddock CD, Sumner JW, Comer JA, Zaki SR, Goldsmith CS, Goddard J, Rickettsia parkeri: a newly recognized cause of spotted fever rickettsiosis in the United States. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38:805–11. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Stenos J, Graves S, Unsworth N. A highly sensitive and specific real-time PCR assay for the detection of spotted fever and typhus group rickettsiae. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2005;73:1083–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fournier PE, Dumler JS, Greub G, Zhang J, Wu Y, Raoult D. Gene sequence-based criteria for identification of new Rickettsia isolates and description of Rickettsia heilonjiangensis sp. nov. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41:5456–65. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24:1596–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Felsenstein J. PHYLIP: Phylogeny Inference Package (Version 3.2). Cladistics. 1989;5:164–6.
- Mediannikov O, Matsumoto K, Samoylenko I, Drancourt M, Roux V, Rydkina E, Rickettsia raoultii sp. nov., a spotted fever group rickettsia associated with Dermacentor ticks in Europe and Russia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2008;58:1635–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vilcins IM, Old JM, Deane E. Detection of a Hepatozoon and spotted fever group Rickettsia species in the common marsupial tick (Ixodes tasmani) collected from wild Tasmanian devils (Sarcophilus harrisii), Tasmania. Vet Parasitol. 2009;162:23–31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: December 08, 2010
Page updated: December 08, 2010
Page reviewed: December 08, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.