Volume 15, Number 12—December 2009
Dispatch
Diagnostic Assay for Rickettsia japonica
Figure
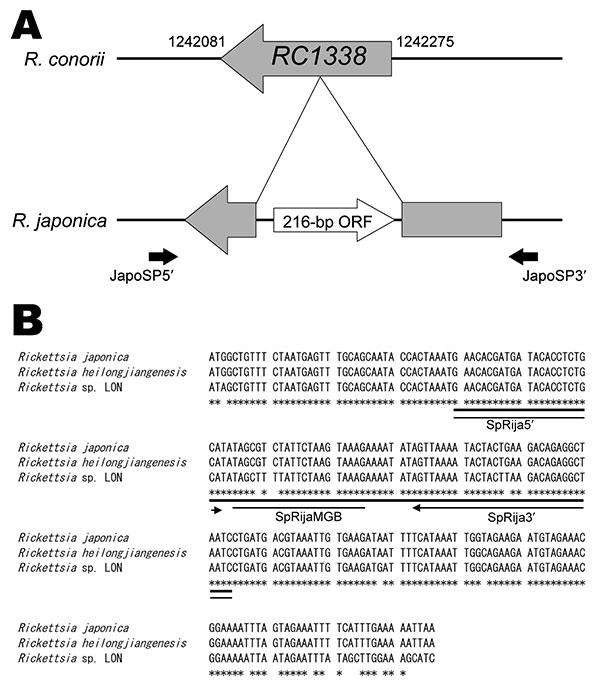
Figure. Unique DNA sequence in the Rickettsia japonica genome that analyzed PCR in this study. A) Comparative genome map of the 216-bp open reading frame (ORF). The R. japonica–specific sequence region (AB437281) in the R. japonica genome and the complete genome sequence of R. conorii strain Malish 7 were compared. The RC1338 DNA sequence and the mapping position data for R. conorii were obtained from the Rickettsia genome database (www.igs.cnrs-mrs.fr/mgdb/Rickettsia). Two solid black arrows indicate primer positions; this region was amplified and sequenced with the same primers. B) Alignments of R. japonica–specific 216-bp ORF (AB437281) between R. japonica YH, R. heilongjiangensis CH8-1, and Rickettsia sp. LON, as performed by the program ClustalW (www.ebi.ac.uk/clustalw), and the positions of primers and probe in real-time PCR. Primer positions and directions (black arrows) and the TaqMan minor groove binder (MGB) (line) probe position are shown. The 216-bp ORF of R. heilongjiangensis and Rickettsia sp. LON were registered on GenBank with accession nos. AB512783 and AB512784, respectively. DNA sequences are identical among R. japonica strains and Rickettsia sp. LON strains (asterisks). The alignment was edited with BioEdit version 7.0.0 (www.mbio.ncsu.edu/BioEdit/bioedit.html).