Volume 15, Number 2—February 2009
Research
Characteristics of 263K Scrapie Agent in Multiple Hamster Species
Figure 6
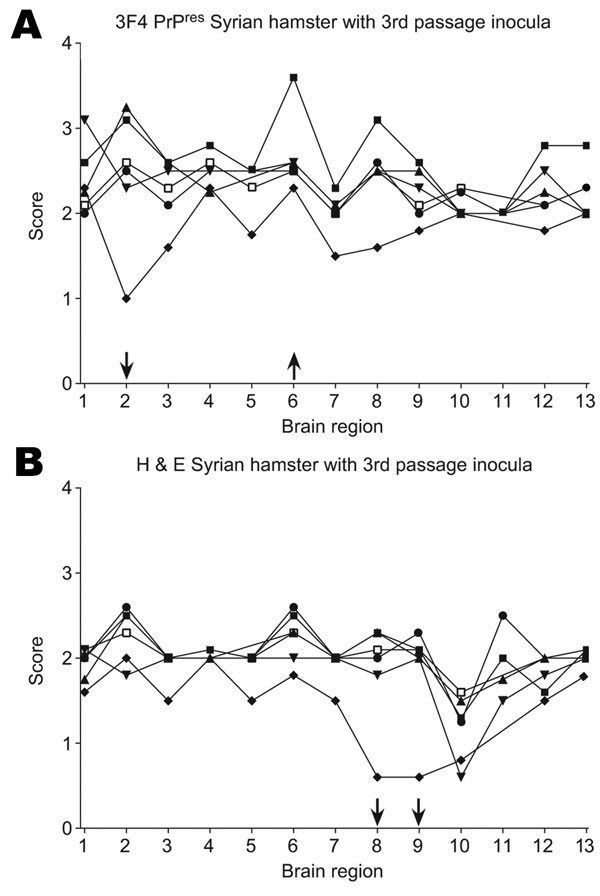
Figure 6. A) Proteinase K–resistant prion protein (PrPres) pathogenicity profiles in Syrian hamsters inoculated with third-passage PrPres. B) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)–stained lesion profiles of Syrian hamsters inoculated with brain homogenate derived from third-passage hamsters. Each point represents the average from 6 different animals scored in the following areas: 1, cerebellum; 2, posterior colliculus; 3, superior colliculus; 4, brain stem; 5, spinal cord; 6, thalamus; 7, hypothalamus; 8, hippocampus; 9, cortex; 10, olfactory bulbs; 11, caudate putamen; 12, septal nucleus; 13, tegmentum. Syrian hamster inoculated with third-passage brain homogenate from the following hamster species: ●, Turkish; ■, Djungarian; ♦, Chinese; ▼, Armenian; ▲, Siberian; □, Syrian. Arrows represent differences in multiple regions indicating increases or decreases in vacuolation or PrPres deposition.