Volume 15, Number 2—February 2009
Dispatch
Vaccine-induced Immunity Circumvented by Typical Mycobacterium tuberculosis Beijing Strains
Figure 1
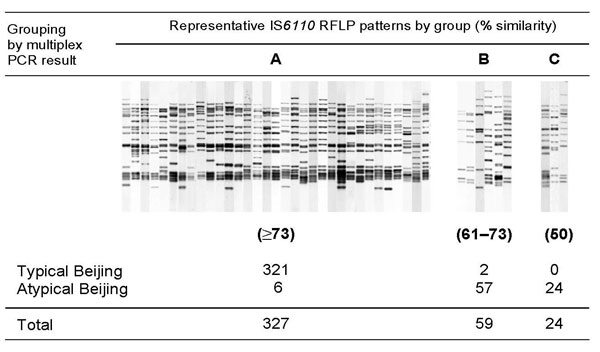
Figure 1. Correlation between the multiplex PCR results and insertion sequence (IS)6110 restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) pattern similarity. On the basis of IS6110 RFLP pattern similarity, 3 groups of related patterns (A, B, and C) were recognized among 410 Mycobacterium tuberculosis Beijing clade strains isolated in the Netherlands. The similarity of the IS6110 RFLP patterns of groups B (61%–73%) and C (50%) are relative to the RFLP patterns of group A. Within group C the similarity of the patterns was at least 58%. By using an IS6110 RFLP similarity of 73% as cutoff (which defined the most homogeneous IS6110 RFLP group [group A]), 321 (98.2%) of 327 Beijing strains were consistently identified as typical Beijing, and 81 (97.6%) of the 83 remaining Beijing clade strains were classified as atypical Beijing by the multiplex PCR. The κ value for agreement between the tests is 0.922.