Volume 16, Number 3—March 2010
Dispatch
Parvovirus 4–like Virus in Blood Products
Figure 2
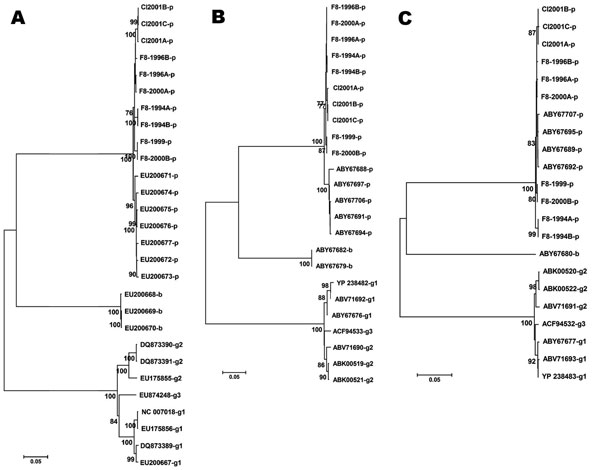
Figure 2. Construction of phylogenic trees for newly identified porcine viruses and comparison with previously identified prototype parvovirus 4 (PARV4)–like sequences. Sequences of other PARV4-like viruses indicated by the accession numbers were obtained from GenBank, and their origins are marked by letters (p, porcine; b, bovine; PARV4-g1, g2, g3, human parvovirus 4 genotypes 1, 2, and 3). ClustalW-aligned genomes (A) and nonstructural (NS) protein (B) and viral protein (VP) (C) were all trimmed to obtain sequences with similar lengths. All computer analysis was performed by using the neighbor-joining method. Branches corresponding to partitions reproduced in <70% bootstrap replicates are collapsed. The tree is drawn to scale, and the percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1,000 replicates) are shown below the branches. F8-year, year of the factor VIII lot; Cl-year, plasma samples and year of collection. Scale bar represents the number of nucleotide (A) or amino acid (B, C) substitutions per site.