Volume 16, Number 8—August 2010
Dispatch
Novel Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex Pathogen, M. mungi
Figure 2
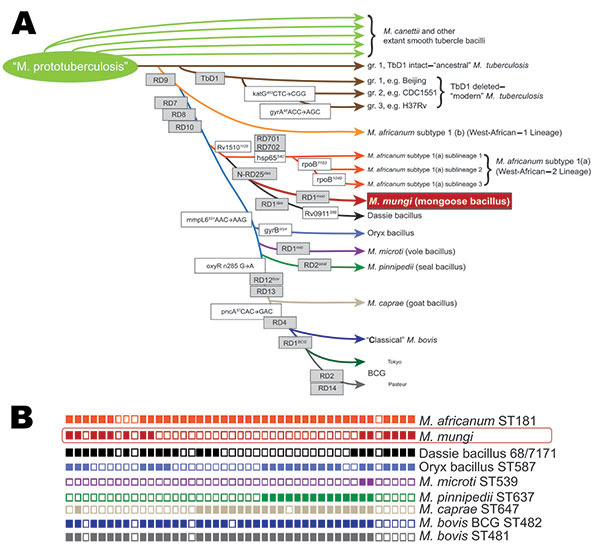
Figure 2. A) Schematic of the phylogenetic relationships among Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex species, including newly discovered M. mungi, based on the presence or absence of regions of difference (gray boxes) as well as specific single-nucleotide polymorphisms (white boxes), modified from (7). B) Spoligotype of M. mungi compared with representative spoligotypes from other M. tuberculosis complex species (8–10).
References
- Alexander K, Pleydell E, Williams M, Lane E, Nyange J, Michel A. Mycobacterium tuberculosis: an emerging disease of free-ranging wildlife. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002;8:598–601.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Liébana E, Aranaz A, Francis B, Cousins D. Assessment of genetic markers for species differentiation within the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. J Clin Microbiol. 1996;34:933.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Harmsen D, Dostal S, Roth A, Niemann S, Rothgänger J, Sammeth M, RIDOM: comprehensive and public sequence database for identification of Mycobacterium species. BMC Infect Dis. 2003;3:26. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Warren R, Gey van Pittius N, Barnard M, Hesseling A, Engelke E, De Kock M, Differentiation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex by PCR amplification of genomic regions of difference. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2006;10:818–22.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Huard R, Fabre M, de Haas P, Claudio Oliveira Lazzarini L, van Soolingen D, Cousins D, Novel genetic polymorphisms that further delineate the phylogeny of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. J Bacteriol. 2006;188:4271. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gordon S, Bottai D, Simeone R, Stinear T, Brosch R. Pathogenicity in the tubercle bacillus: molecular and evolutionary determinants. Bioessays. 2009; 31.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kremer K, Van Soolingen D, Frothingham R, Haas W, Hermans P, Martin C, Comparison of methods based on different molecular epidemiological markers for typing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains: interlaboratory study of discriminatory power and reproducibility. J Clin Microbiol. 1999;37:2607.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Brudey K, Driscoll J, Rigouts L, Prodinger W, Gori A, Al-Hajoj S, Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex genetic diversity: mining the fourth international spoligotyping database (SpolDB 4) for classification, population genetics and epidemiology. BMC Microbiol. 2006;6:23. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- van Soolingen D, van der Zanden A, de Haas P, Noordhoek G, Kiers A, Foudraine N, Diagnosis of Mycobacterium microti infections among humans by using novel genetic markers. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36:1840.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mostowy S, Onipede A, Gagneux S, Niemann S, Kremer K, Desmond E, Genomic analysis distinguishes Mycobacterium africanum. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:3594. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kamerbeek J, Schouls L, Kolk A, Van Agterveld M, Van Soolingen D, Kuijper S, Simultaneous detection and strain differentiation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis for diagnosis and epidemiology. J Clin Microbiol. 1997;35:907.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Supply P, Allix C, Lesjean S, Cardoso-Oelemann M, Rusch-Gerdes S, Willery E, Proposal for standardization of optimized mycobacterial interspersed repetitive unit–variable-number tandem repeat typing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44:4498. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sousa A, Salem J, Lee F, Vercosa M, Cruau P, Bloom B, An epidemic of tuberculosis with a high rate of tuberculin anergy among a population previously unexposed to tuberculosis, the Yanomami Indians of the Brazilian Amazon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94:13227–23. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: March 30, 2011
Page updated: March 30, 2011
Page reviewed: March 30, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.