Volume 12, Number 7—July 2006
Letter
Panton-Valentine Leukocidin Genes in Staphylococcus aureus
Cite This Article
Citation for Media
The pathogenicity of Staphylococcus aureus depends on various bacterial surface components and extracellular proteins. However, the precise role of single virulence determinants in relation to infection is hard to establish. The frequent recovery of staphylococcal isolates that produce leukocidal toxins from patients with deep skin and soft tissue infections, particularly furunculosis, cutaneous abscesses, and severe necrotizing pneumonia, suggests that the Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL) is 1 such virulence factor that has a major role in pathogenicity (1–3).
In 1932, Panton and Valentine described PVL as a virulence factor belonging to the family of synergohymenotropic toxins (4). These toxins form pores in the membrane of host defense cells by synergistic action of 2 secretory proteins, designated LukS-PV and LukF-PV, which are encoded by 2 cotranscribed genes of a prophage integrated in the S. aureus chromosome (5). PVL is mostly associated with community-acquired methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) infections and distinguishable from nosocomial MRSA by nonmultidrug resistance and carriage of the type IV staphylococcal chromosome cassette element (SCCmec type IV) (6,7).
Despite the presumed importance of PVL as a virulence factor, few data are available on its prevalence among S. aureus isolates from the nares of healthy persons compared with stains isolated from infections. This lack of data led us to investigate the frequency of PVL gene–positive S. aureus strains obtained from the nares of healthy carriers in the community. For this purpose, a single polymerase chain reaction method was used to detect both lukS-PV and lukF-PV genes (2).
In a previous study, the population structure of S. aureus, isolated from the nares of healthy persons in the Rotterdam area, the Netherlands, was elucidated (8). Strains were obtained from healthy children (<19 years) and elderly persons (>55 years). Invasive strains (blood culture, skin and soft tissue infections, and impetigo isolates) were included in this study (Table). All carriage and clinical isolates (n = 1,033) were mecA negative. We used the same strain collection to study the PVL prevalence in carriage and invasive isolates of S. aureus from a single geographic region.
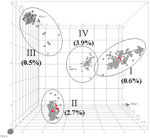
Five PVL-positive S. aureus strains (0.6%) were found in the carriage group (n = 829), and 3 (2.1%) of 146 blood-culture isolates carried the PVL gene (Table). This finding is in agreement with previously reported low PVL prevalences by Prevost et al. (0% in 31 carriage isolates and 1.4% in 69 blood-culture isolates) and Von Eiff et al. (1.4% in 210 carriage isolates and 0.9% in 219 blood-culture isolates) (9,10). However, a higher prevalence of PVL (38.9%) was found in S. aureus strains causing abscesses and arthritis (Fisher exact test, p <0.0001) (8). This finding is also in agreement with the proposed involvement of PVL in severe and invasive (soft tissue) staphylococcal infections (1–3). No significant differences were found in the presence of PVL when carriage isolates were compared with invasive blood-culture isolates. PVL was found in each major genomic amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) cluster, indicating that PVL has been introduced in distinct phylogenetic subpopulations of S. aureus (Figure). Multilocus sequence typing analysis of a subset of the strain collection showed that the 15 PVL-positive strains were within clonal complex (CC) 30 (n = 7), CC 121 (n = 3), CC 1 (n = 2), CC 8 (n = 1), CC 22 (n = 1), and CC 45 (n = 1) (Table) (8). Although PVL was found among several staphylococcal genotypes, it was slightly overrepresented in AFLP cluster IVb (CC 121) compared with major clusters I and III. Whether the prevalence of PVL in carriage- and blood-culture isolates is higher and differs among distinct genetic clusters of S. aureus in countries with endemic CA-MRSA has to be investigated further.
In conclusion, we have shown that the PVL-encoding phage has entered distinct staphylococcal lineages, although its prevalence differs per clonal group. PVL is associated with skin and soft tissue infections but not with bacteremia, which suggests that PVL is not likely to be involved in the pathogenesis of bacteremia. Infections caused by PVL-positive S. aureus strains have been documented since the 1930s. Expansion and increased incidence of such infections, however, are more recent, and further epidemiologic studies for tracking this phenomenon are still warranted.
References
- Gillet Y, Issartel B, Vanhems P, Fournet JC, Lina G, Bes M, Association between Staphylococcus aureus strains carrying gene for Panton-Valentine leukocidin and highly lethal necrotising pneumonia in young immunocompetent patients. Lancet. 2002;359:753–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lina G, Piemont Y, Godail-Gamot F, Bes M, Peter MO, Gauduchon V, Involvement of Panton-Valentine leukocidin-producing Staphylococcus aureus in primary skin infections and pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;29:1128–32. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Holmes A, Ganner M, McGuane S, Pitt TL, Cookson BD, Kearns AM. Staphylococcus aureus isolates carrying Panton-Valentine leucocidin genes in England and Wales: frequency, characterization, and association with clinical disease. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43:2384–90. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Prevost G, Cribier B, Couppie P, Petiau P, Supersac G, Finck-Barbancon V, Panton-Valentine leucocidin and gamma-hemolysin from Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 49775 are encoded by distinct genetic loci and have different biological activities. Infect Immun. 1995;63:4121–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Miller LG, Perdreau-Remington F, Rieg G, Mehdi S, Perlroth J, Bayer AS, Necrotizing fasciitis caused by community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Los Angeles. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1445–53. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vandenesch F, Naimi T, Enright MC, Lina G, Nimmo GR, Heffernan H, Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying Panton-Valentine leukocidin genes: worldwide emergence. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9:978–84.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Melles DC, Gorkink RF, Boelens HA, Snijders SV, Peeters JK, Moorhouse MJ, Natural population dynamics and expansion of pathogenic clones of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Invest. 2004;114:1732–40.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Prevost G, Couppie P, Prevost P, Gayet S, Petiau P, Cribier B, Epidemiological data on Staphylococcus aureus strains producing synergohymenotropic toxins. J Med Microbiol. 1995;42:237–45. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- von Eiff C, Friedrich AW, Peters G, Becker K. Prevalence of genes encoding for members of the staphylococcal leukotoxin family among clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2004;49:157–62. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Figure
Table
Cite This ArticleRelated Links
Table of Contents – Volume 12, Number 7—July 2006
| EID Search Options |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Please use the form below to submit correspondence to the authors or contact them at the following address:
D.C. Melles, Erasmus MC, University Medical Center Rotterdam, Department of Medical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases, Rm L-313, Dr Molewaterplein 40, 3015 GD Rotterdam, the Netherlands
Top