Volume 13, Number 7—July 2007
Synopsis
Thottapalayam Virus, a Prototype Shrewborne Hantavirus
Figure 3
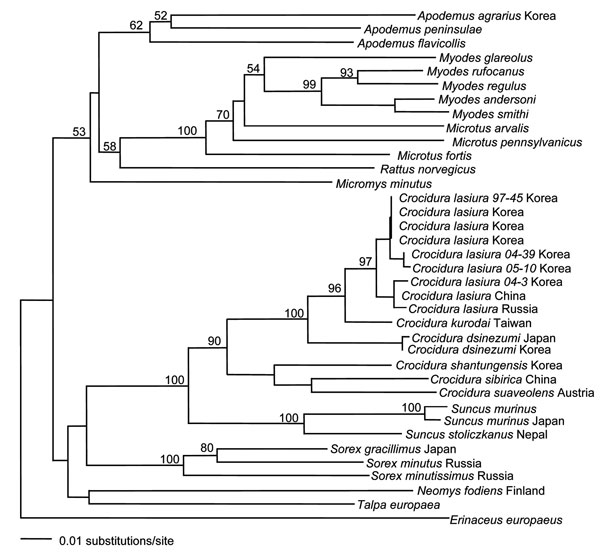
Figure 3. Phylogenetic relationship between Suncus murinus and other insectivores and rodents in a 401-nt cytochrome b region of mitochondrial DNA determined by using the neighbor-joining method. Numbers at each node are bootstrap probabilities determined for 1,000 iterations. Members of the genus Crocidura (white-toothed shrews) belong to the subfamily Crocidurinae. They are distinguished from members of the subfamily Soricinae (red-toothed shrews) by their unpigmented teeth, 3 upper unicuspids, and more prominent ears than either the genera Sorex or Neomys.
Page created: June 21, 2010
Page updated: June 21, 2010
Page reviewed: June 21, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.