Volume 13, Number 9—September 2007
Dispatch
Coronavirus Antibodies in African Bat Species
Cite This Article
Citation for Media
Abstract
Asian bats have been identified as potential reservoir hosts of coronaviruses associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV). We detected antibody reactive with SARS-CoV antigen in 47 (6.7%) of 705 bat serum specimens comprising 26 species collected in Africa; thus, African bats may harbor agents related to putative group 4 CoV.
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) emerged as a newly recognized human disease in the People’s Republic of China late in 2002 and spread globally, causing 8,422 infections with 916 (11%) deaths before it was brought under control in 2003 (1). The causative agent was identified as a coronavirus (SARS-CoV) (2–4), and related viruses found in palm civets (Paguma larvata), raccoon dogs (Nycereutes procyonoides) (5), and insectivorous bats in Asia cluster phylogenetically together with SARS-CoV in a putative group 4 (6–10). Farmed food animals such as civets may acquire SARS-like-CoV infection from bats, and adaptation of the viruses to these secondary hosts may occasionally give rise to strains capable of spreading and causing disease in humans (HCoV) (10).
Bat serum specimens (n = 705) collected from 1986 through 1999 in South Africa (SA) and the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) were tested. The first 248 serum specimens were collected from 1986 through 1989 in the Mpumalanga and Limpopo Provinces of SA for studies on rabies-related viruses, with the approval of the provincial Directorates of Nature Conservation and the Animal Ethics Committee of the University of the Witwatersrand. The remaining 457 serum samples were collected in 1995–1999 in the Bandundu and Oriental Provinces of the DRC for studies on Ebola and Marburg viruses, under the auspices of the International Committees for the Control of Ebola hemorrhagic fever in Kikwit, and Marburg hemorrhagic fever in Durba-Watsa, coordinated by the World Health Organization on behalf of the government of DRC. Bats were caught in mist nets, anesthetized, and exsanguinated by cardiac puncture. Serum specimens were stored at –70°C until analyzed.
For screening of serum specimens we used the SARS-CoV ELISA kit (EUROIMMUN AG, Lübeck, Germany) with minor modifications. Bat serum samples were tested at a dilution of 1:50, and horseradish peroxidase–labeled goat antibat immunoglobulin (Ig) conjugate (Bethyl, Montgomery, AL, USA) was used as secondary antibody at a dilution of 1:2,000. Negative bat serum was obtained from a captive-bred Rousettus aegyptiacus at the National Institute for Communicable Diseases, Sandringham, SA. The cut-off was determined as 3× the mean optical density value at 450/605 nm observed in negative control samples. Positive serum samples were retested and their titers determined. To evaluate test specificity and to exclude possible cross-reactivity to other viruses, especially to HCoVs, which have a seroprevalence in humans >90% (11), 662 human serum specimens were screened (Technical Appendix), including those from 90 patients with other acute respiratory infections, 70 HCoV-229E–positive serum specimens and 4 HCoV-NL63–positive serum specimens (provided by L. van der Hoek).
A confirmatory Western blot (WB) was done by using protein lysates from Vero E6 cell cultures (American Type Culture Collection [Manassas, VA, USA] CRL 1586) infected with SARS-CoV Hong Kong isolate 6109 (GenBank accession no. AY278491) and from uninfected Vero E6 cultures. Bat serum specimens were applied at dilutions of 1:500 and 1:2,000. Secondary detection was performed with the SuperSignal West Dura Extended Substrate chemiluminescence detection assay (Pierce Biotechnology, Rockford, IL, USA). The signal intensity of the 150-kDa spike (S), 50-kDa nucleocapsid (N) proteins was evaluated independently by 2 operators. For a second confirmatory WB, recombinant SARS-CoV proteins were used. For prokaryotic expression of recombinant SARS-CoV N protein and a fragment of the spike S protein (amino acid positions 318–510), we followed the instructions of the Champion pET Directional TOPO Expression kit (Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany) using plasmids pET101-N and pET102-Saa318–510. Purification and refolding of the protein on column were done as described previously (12). Purified recombinant protein (15 μg) was resolved by electrophoresis on a discontinuous 12% sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel. After blotting, nitrocellulose strips were incubated with bat serum samples diluted 1:2,500 and 1:5,000. One positive bat serum specimen was used as a reference to exclude variations in experimental procedures and signal intensities. Serum specimens that produced signals at a dilution 1:5,000 were considered positive as none of the control serum specimens showed reactivity at that dilution. To evaluate assay specificity, we tested 19 control serum specimens comprising 12 randomly selected bat serum specimens that were negative by ELISA, 2 SARS-CoV–positive human serum specimens, and 5 SARS-CoV–negative human serum specimens, including 4 HCoV-NL63–positive serum specimens.
A commercial indirect immunofluorescence test (SARS-CoV-IFTII kit, EUROIMMUN AG) was carried out as described by the manufacturer, except that bat serum samples were diluted 1:100, and slides were incubated at room temperature for 2 hours. Reactions were detected with goat-antibat immunogolublin (Ig) (Bethyl) at a dilution of 1:1,000 and fluorescein isothiocyanate–labeled donkey-antigoat Ig (Dianova, Hamburg, Germany) at a dilution of 1:100. Specificity of the indirect immunofluorescence test (IIFT) was determined by screening 572 human serum specimens. The sensitivity and correlation of IIFT versus ELISA were analyzed (Technical Appendix). In addition, the 19 selected control serum samples were tested.
Virus neutralization tests were performed as described elsewhere (13) except for using Vero E6 cells cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium and SARS-CoV Hong Kong isolate 6109 (3.25 × 107 PFU/mL, diluted 1:5,000). Bat serum dilutions in quadruplicate ranged from 1:10 to 1:320. After incubation at 37°C in 5% CO2 for 3 days, the cells were fixed with 8% formaldehyde and results interpreted as described (13).
Viral RNA was extracted from serum by using a QIAamp viral RNA extraction kit (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany), and reverse transcription–PCR (RT-PCR) was performed essentially as described elsewhere (14), with the exception that 140 μL was not available from every bat. In such cases, input volume was reduced and replaced with water. A minimum of 20 μL was usually tested.
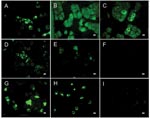
Antibody activity to SARS-CoV antigen was detected by ELISA in 7 of 26 bat species tested at both collection sites with a seroprevalence of 6.7% (47/705). The highest prevalences were found in the fruit bat Rousettus aegyptiacus (Chiroptera: Pteropodidae) (16.4%) and the insectivorous bat Mops condylurus (Chiroptera: Molossidae) (12.2%) (Table). ELISA titers ranged from 50 (73% of the serum samples) to 800. Confirmatory WB analyses performed by 2 methods on ELISA-positive samples for which sufficient material remained available, were positive in 36 (97.3%) of 37 serum specimens, but IIFT was positive in only 12 (32.4%) of 37 samples (Table; Figures 1, 2; Figure in Technical Appendix). None of the assays used detected antibodies to other human pathogenic coronaviruses (Technical Appendix; Figures 1, 2). Neutralizing activity to SARS-CoV was not found in any of the ELISA-positive samples, and RT-PCR did not detect CoV nucleic acid in 262 serum specimens tested (data not shown).
The results of WB analyses support the specificity of the ELISA used in this study. The IF test is known to be less sensitive than ELISA but still provided confirmation in one third of the serum specimens tested. The negative results in the viral neutralization tests are not unexpected because this assay detects only antibodies that interfere with the specific entry mechanism of SARS-CoV, and putative group 4 CoVs from African bats may not use it. Moreover, deletions and mutations found in Asian bat SARS-like–CoV isolates lie in the S protein region essential for binding of SARS-CoV to the cellular receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, and thus are likely to affect cross-neutralization, as emphasized by conflicting results obtained in Asia (6,7,15). The negative findings obtained in RT-PCR can be explained by the unlikelihood of finding virus nucleic acid in serum. Studies in Asia used rectal swabs instead of serum samples, and the virus likely persists in the enteric tract but may not be found in serum at all.
Both bat species (R. aegyptiacus and M. condylurus) are widely distributed in Africa but vary in the degree of contact with humans. R. aegyptiacus roosts in caves but forages in orchards, whereas M. condylurus roosts in buildings. The results of this preliminary study suggest that some of the African bat species harbor agents related to putative group 4 CoV, and therefore further investigations should be undertaken to determine potential public health risks.
Mr Müller is a scientist at the Center for Biological Safety of the Robert Koch-Institut, Berlin. He has been involved in establishing diagnostic tools for SARS-CoV detection, assisted international quality assurance studies on SARS diagnostics, and worked on SARS-CoV susceptibility studies. Currently he is finishing his PhD thesis on expression analysis of coronavirus structural proteins.
Acknowledgment
We thank A. Teichmann for excellent technical assistance. We also thank Lia van der Hoek for providing us with HCoV-NL63–positive serum specimens.
References
- Peiris JS, Lai ST, Poon LL, Guan Y, Yam LY, Lim W, Coronavirus as a possible cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Lancet. 2003;361:1319–25. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Drosten C, Gunther S, Preiser W, van der Werf S, Brodt HR, Becker S, Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1967–76. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ksiazek TG, Erdman D, Goldsmith CS, Zaki SR, Peret T, Emery S, A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1953–66. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Guan Y, Zheng BJ, He YQ, Liu XL, Zhuang ZX, Cheung CL, Isolation and characterization of viruses related to the SARS coronavirus from animals in southern China. Science. 2003;302:276–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Li W, Shi Z, Yu M, Ren W, Smith C, Epstein JH, Bats are natural reservoirs of SARS-like coronaviruses. Science. 2005;310:676–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lau SK, Woo PC, Li KS, Huang Y, Tsoi HW, Wong BH, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-like virus in Chinese horseshoe bats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:14040–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tang XC, Zhang JX, Zhang SY, Wang P, Fan XH, Li LF, Prevalence and genetic diversity of coronaviruses in bats from China. J Virol. 2006;80:7481–90. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Calisher CH, Childs JE, Field HE, Holmes KV, Schountz T. Bats: important reservoir hosts of emerging viruses. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006;19:531–45. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wang LF, Shi Z, Zhang S, Field H, Daszak P, Eaton BT. Review of bats and SARS. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:1834–40.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hofmann H, Pyrc K, van der Hoek L, Geier M, Berkhout B, Pöhlmann S. Human coronavirus NL63 employs the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus receptor for cellular entry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:7988–93. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Oganesyan N, Kim SH, Kim R. On-column protein refolding for crystallization. J Struct Funct Genomics. 2005;6:177–82. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Niedrig M, Lademann M, Emmerich P, Lafrenz M. Assessment of IgG antibodies against yellow fever virus after vaccination with 17D by different assays: neutralization test, haemagglutination inhibition test, immunofluorescence assay and ELISA. [PMID: 17229859]. Trop Med Int Health. 1999;4:867–71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- de Souza Luna LK, Heiser V, Regamey N, Panning M, Drexler JF, Mulangu S, Generic detection of coronaviruses and differentiation at the prototype strain level by reverse transcription PCR and nonfluorescent low-density microarray. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45:1049–52. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sui J, Li W, Roberts A, Matthews LJ, Murakami A, Vogel L, Evaluation of human monoclonal antibody 80R for immunoprophylaxis of severe acute respiratory syndrome by an animal study, epitope mapping, and analysis of spike variants. J Virol. 2005;79:5900–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Figures
Table
Cite This ArticleTable of Contents – Volume 13, Number 9—September 2007
| EID Search Options |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Please use the form below to submit correspondence to the authors or contact them at the following address:
Marcel A. Müller, Robert Koch-Institut, Center for Biological Safety, ZBS-1, Nordufer 20, 13353 Berlin, Germany;
Top