Volume 14, Number 11—November 2008
Dispatch
Use of Malaria Rapid Diagnostic Test to Identify Plasmodium knowlesi Infection
Figure 1
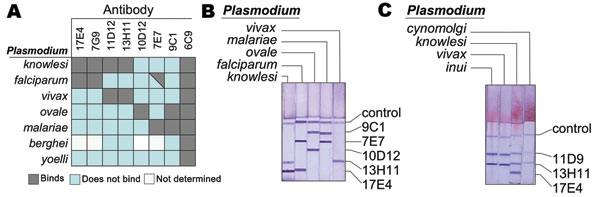
Figure 1. Binding specificity of different anti–Plasmodium lactate dehydrogenase (pLDH) antibodies. A) Shown are the reactivities of the indicated monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) to the LDH from 7 Plasmodium spp. Reactivity was determined by using an immunocapture assay as previously described (9). B) Example of an immunodipstick assay that detects P. knowlesi. An immunochromatographic strip assay containing the indicated antibodies was allowed to wick lysed blood infected with P. vivax, P. falciparum, P. knowlesi, P. ovale, or P. malariae. Blood was wicked in the presence of colloidal gold conjugated to antibody 6C9, which binds all pLDH isoforms. P. vivax LDH is immobilized only by 11D9 and 13H11, and P. falciparum LDH was only immobilized by 17E4. P. knowlesi LDH was immobilized by 11D9 and 13H11 antibodies and also by 17E4. C) An immunochromatographic strip assay containing the indicated antibodies was allowed to wick lysed blood infected with P. vivax, P. cynomolgi, P. inui, and P. knowlesi. Blood was wicked in the presence of colloidal gold conjugated to antibody 6C9, which binds all pLDH isoforms. Both P. cynomolgi and P. inui show the same epitope profile as P. vivax.
References
- Singh B, Kim Sung L, Matusop A, Radhakrishnan A, Shamsul SS, Cox-Singh J, A large focus of naturally acquired Plasmodium knowlesi infections in human beings. Lancet. 2004;363:1017–24. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cox-Singh J, Davis TM, Lee KS, Shamsul SS, Matusop A, Ratnam S, Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in humans is widely distributed and potentially life threatening. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46:165–71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jongwutiwes S, Putaporntip C, Iwasaki T, Sata T, Kanbara H. Naturally acquired Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in human, Thailand. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:2211–3.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ng OT, Ooi EE, Lee CC, Lee PJ, Ng LC, Pei SW, Naturally acquired human Plasmodium knowlesi infection, Singapore. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:814–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Luchavez J, Espino F, Curameng P, Espina R, Bell D, Chiodini P, Human infections with Plasmodium knowlesi, the Philippines. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:811–3.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Knowles R, White RS. Studies in the parasitology of malaria. Indian Med Res Memoirs No. 18, Calcutta (India): Thacker, Spink, and Co.; 1930.
- Cohen JE. Heterologous immunity in human malaria. Q Rev Biol. 1973;48:467–89. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chin W, Contacos PG, Collins WE, Jeter MH, Alpert E. Experimental mosquito-transmission of Plasmodium knowlesi to man and monkey. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1968;17:355–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Eyles DE, Coatney GR, Getz ME. Vivax-type malaria parasites of macaques transmissible to man. Science. 1960;131:1812–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Baimai V. Population cytogenetics of the malaria vector Anopheles leucosphyrus group. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1988;19:667–80.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Brown WM, Yowell CA, Hoard A, Vander Jagt TA, Hunsaker LA, Deck LM, Comparative structural analysis and kinetic properties of lactate dehydrogenases from the four species of human malarial parasites. Biochemistry. 2004;43:6219–29. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Piper R, Lebras J, Wentworth L, Hunt-Cooke A, Houzé S, Chiodini P, Immunocapture diagnostic assays for malaria using Plasmodium lactate dehydrogenase (pLDH). Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1999;60:109–18.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Torda AE, Procter JB, Huber T. Wurst: a protein threading server with a structural scoring function, sequence profiles and optimized substitution matrices. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:W532–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Boyd MF, Kitchen SF. Simultaneous inoculation with Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium falciparum. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1937;17:855–61.
- Boyd MF, Kitchen SF, Matthews CB. Consecutive inoculations with Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium falciparum. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1938;18:141–50.