Volume 14, Number 5—May 2008
Dispatch
Spread of Streptococcus suis Sequence Type 7, China
Figure 2
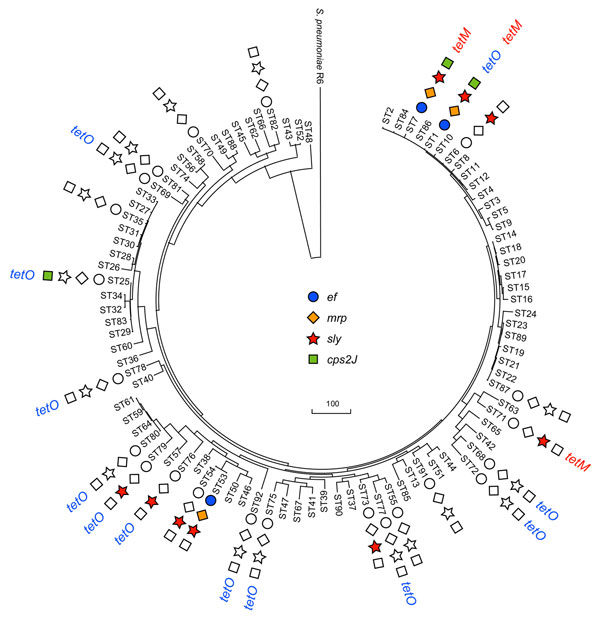
Figure 2. Horizontal transfer events of virulence genes and conjugative transposon Tn916 with tetM in Streptococcus suis sequence types. The rooted maximum-parsimony tree was based on the concatenated sequences of 7 housekeeping genes used for multilocus sequence typing analysis of S. suis by using S. pneumoniae R6 as the outgroup. Virulence genes acquired by strains of various sequence types were from this study and other published papers. The colored labels indicate positive detection; uncolored labels indicate negative results for the virulence gene; no label indicates that the strain was not available for testing. The scale bar indicates a branch length corresponding to 100 character-state changes.
Page created: July 08, 2010
Page updated: July 08, 2010
Page reviewed: July 08, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.