Volume 15, Number 9—September 2009
Research
Genetics and Pathogenesis of Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus
Appendix Figure 2
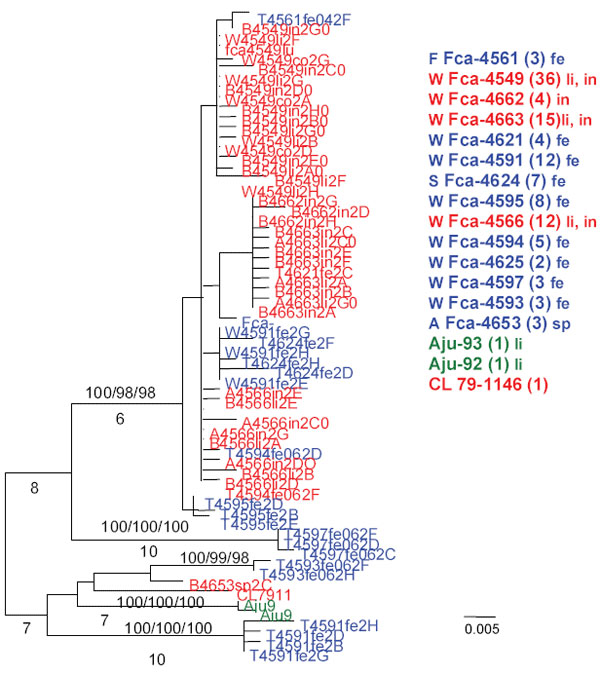
Appendix Figure 2. Midpoint rooted maximum likelihood (ML) tree of unique pol1a 386-bp sequences (ML -ln L = 1300.12586 best tree found by maximum parsimony: length = 125, confidence interval = 0.832, retention index = 0.926). Cloned sequences from feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) cases are shown in red, feline enteric coronavirus (FECV) asymptomatic cats are shown in blue, and feline coronavirus (FCoV) virulent strain from Aju-92 (cheetah) is in green. Each sequence is labeled as follows: source farm (W, Weller Farm; F, Frederick Animal Shelter; S, Seymour Farm; M, Mount Airy Shelter; A, Ambrose Farm), 4-digit cat identification number, tissue source (fe, feces; af, ascites fluid; co, colon; li, liver; sp, spleen; in, intestine; je, jejunum; ln, lymph node), 2-digit year (e.g., 04 = 2004), and number of clones for each sequence. Scale bar indicates number of substitutions per site.