Volume 16, Number 8—August 2010
Research
White-Nose Syndrome Fungus (Geomyces destructans) in Bats, Europe
Figure 2
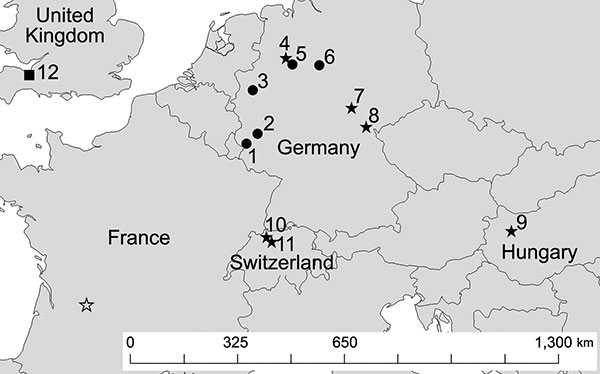
Figure 2. Locations in Europe of bats positive for Geomyces destructans by PCR alone (circles) or by PCR and culture (solid stars) and bats negative for G. destructans but positive for other fungi (square). Numbers for locations correspond to those in Table 2. Sites 7, 8, and 9 had additional bats that were positive for G. destructans only by PCR. Location of a bat positive for G. destructans in France (16) is indicated by an open star. Some sites had >1 bat species with evidence of colonization by G. destructans.
References
- Blehert DS, Hicks AC, Behr M, Meteyer CU, Berlowski-Zier BM, Buckles EL, Bat white-nose syndrome: an emerging fungal pathogen? Science. 2009;323:227. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Reichard JD, Kunz TH. White-nose syndrome inflicts lasting injuries to the wings of little brown myotis (Myotis lucifugus). Acta Chiropt. 2009;11:457–64. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Turner GR, Reeder DM. Update of white-nose syndrome in bats, September 2009. Bat Research News. 2009;50:47–53.
- Courtin F, Stone W, Risatti G, Gilbert K, Van Kruiningen H. Pathologic findings and liver elements in hibernating bats with white-nose syndrome. Vet Pathol. 2010;47:214–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- United States Geological Survey. Update on white-nose syndrome: Tennessee finding. USGS wildlife health bulletin. Reston (VA): The Survey; 2010 [cited 2010 May 19]. http://www.nwhc.usgs.gov/disease_information/white-nose_syndrome/
- Gargas A, Trest MT, Christensen M, Volk TJ, Blehert DS. Geomyces destructans sp. nov. associated with bat white-nose syndrome. Mycotaxon. 2009;108:147–54. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Meteyer CU, Buckles EL, Blehert DS, Hicks AC, Green DE, Shearn-Bochsler V, Histopathologic criteria to confirm white-nose syndrome in bats. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2009;21:411–4.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chabasse D, Guiguen C, Couatarmanac’h A, Launay H, Reecht V, de Bièvre C. Keratinophilic fungal flora isolated from small wild mammals and rabbit-warren in France. Discussion on the fungal species found [in French]. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp. 1987;62:357–68.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mercantini R, Marsella R, Prignano G, Moretto D, Marmo W, Leonetto F, Isolation of keratinophilic fungi from the dust of ferry boats and trains in Italy. Mycoses. 1989;32:590–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- de Bellis T, Kernaghan G, Widden P. Plant community influences on soil microfungal assemblages in boreal mixed-wood forests. Mycologia. 2007;99:356–67. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kochkina GA, Ivanushkina NE, Akimov VN, Gilichinskii DA, Ozerskaia SM. Halo- and psychrotolerant Geomyces fungi from arctic cryopegs and marine deposits [in Russian]. Mikrobiologiia. 2007;76:39–44.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mercantini R, Marsella R, Cervellati M. Keratinophilic fungi isolated from Antarctic soil. Mycopathologia. 1989;106:47–52. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gianni C, Caretta G, Romano C. Skin infection due to Geomyces pannorum var. pannorum. Mycoses. 2003;46:430–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zelenková H. Geomyces pannorum as a possible causative agent of dermatomycosis and onychomycosis in two patients. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2006;14:21–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Feldmann R. Teichfledermaus–Myotis dasycneme (Boie, 1825). Die Säugetiere Westfalens. Münster: Westfälisches Museum für Naturkunde; 1984. p. 107–11.
- Puechmaille SJ, Verdeyroux P, Fuller H, Ar Gouilh M, Bekaert M, Teeling EC. White-nose syndrome fungus (Geomyces destructans) in bat, France. Emerg Infect Dis. 2010;16:290–3.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- White T, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TH, editors. PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. San Diego (CA): Academic Press; 1990. p. 315–22.
- Gargas A, Taylor J. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primers for amplifying and sequencing 18S rDNA from lichenized fungi. Mycologia. 1992;84:589–92. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Gargas A, dePriest P, Taylor J. Positions of multiple insertions in SSU rDNA of lichen forming fungi. Mol Biol Evol. 1995;12:208–18.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lorch JM, Gargas A, Meteyer CU, Berlowski-Zier BM, Green DE, Shearn-Bochsler V, Rapid polymerase chain reaction diagnosis of white-nose syndrome in bats. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2010;22:224–30.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Barlow A, Ford S, Green R, Morris C, Reaney S. Investigations into suspected white-nose syndrome in two bats in Somerset. Vet Rec. 2009;165:481–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hutterer R, Ivanova T, Meyer-Cords C, Rodrigues L. Bat migrations in Europe: a review of banding data and literature. Bonn (Germany): German Agency for Nature Conservation; 2005.
- Nowak R. Walker’s mammals of the world. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press; 1999.
- Dietz C, von Helversen O, Nill D. Bats of Britain, Europe and Northwest Africa. London: A and C Black Publishers; 2009.
- Barbour RW, Davis WH. Bats of America. Lexington (KY): The University Press of Kentucky; 1969.
- Petermann R, Boye P. National report on bat conservation in the Federal Republic of Germany 2003–2006. Bonn (Germany): Eurobats; 2006.
- Casadevall A. Fungal virulence, vertebrate endothermy, and dinosaur extinction: is there a connection? Fungal Genet Biol. 2005;42:98–106. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Desprez-Loustau ML, Robin C, Buée M, Courtecuisse R, Garbaye J, Suffert F, The fungal dimension of biological invasions. Trends Ecol Evol. 2007;22:472–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Robert VA, Casadevall A. Vertebrate endothermy restricts most fungi as potential pathogens. J Infect Dis. 2009;200:1623–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fisher MC, Garner TW, Walker SF. Global emergence of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis and amphibian chytridiomycosis in space, time, and host. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2009;63:291–310. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Voyles J, Young S, Berger L, Campbell C, Voyles WF, Dinudom A, Pathogenesis of chytridiomycosis, a cause of catastrophic amphibian declines. Science. 2009;326:582–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Davis WH. Hibernation: ecology and physiological ecology. In: Wimsatt WA, editor. Biology of bats. Vol. 1. New York: Academic Press; 1970. p. 265–300.
- Makanya AN, Mortola JP. The structural design of the bat wing web and its possible role in gas exchange. J Anat. 2007;211:687–97. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Calisher CH, Childs JE, Field HE, Holmes KV, Schountz T. Bats: an important reservoir host of emerging viruses. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006;19:531–45. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wibbelt G, Speck S, Field H. Methods for assessing diseases in bats. In: Kunz T, Parsons S, editors. Ecological and behavioral methods for the study of bats. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press; 2009. p. 775–94.
Page created: March 30, 2011
Page updated: March 30, 2011
Page reviewed: March 30, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.