Volume 17, Number 8—August 2011
Research
Seroprevalence of Trichodysplasia Spinulosa–associated Polyomavirus
Figure 4
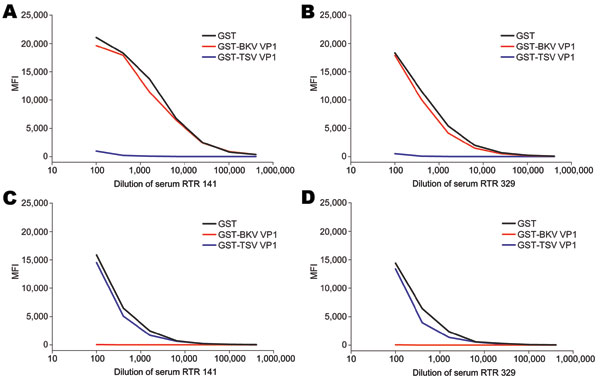
Figure 4. Cross-competition between trichodysplasia spinulosa–associated polyomavirus (TSV) and BKV polyomavirus viral protein 1 (VP1) in serial dilutions of serum samples RTR 141 and RTR 329 from renal transplant recipient patients reactive against TSV VP1 and BKV VP1, the Netherlands. Reactivity was determined by using the VP1 multiplex antibody-binding assay. Samples were preincubated with soluble recombinant glutathione-S-transferase (GST) (black line), GST-BKV VP1 (red line), or GST-TSV VP1 (blue line). Values are median fluorescent intensity (MFI) for seroreactivity against TSV VP1 (A and B) or BKV VP1 (C and D).
Page created: August 15, 2011
Page updated: August 15, 2011
Page reviewed: August 15, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.