Volume 18, Number 10—October 2012
Research
WU and KI Polyomaviruses in Respiratory Samples from Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Recipients
Figure 3
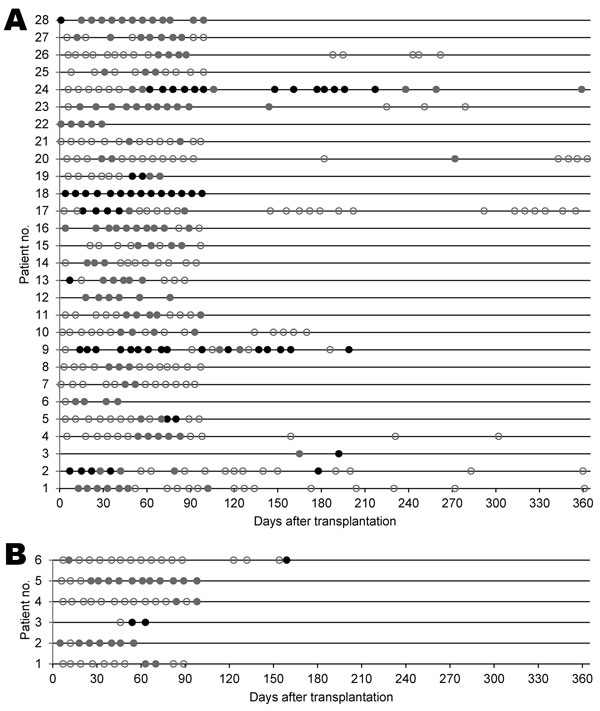
Figure 3. . . . Detection of A) KI polyomavirus (KIPyV) DNA in 28 hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) recipients with >2 KIPyV-positive specimens and B) WU polyomavirus (WUPyV) DNA in 6 HCT recipients with >2 WUPyV-positive specimens, with and without detection of a respiratory virus by day after transplantation. Each line represents 1 patient in order of age (KIPyV-positive patients 1–10 and WUPyV-positive patients 1 and 2 are <20 years of age). Circles indicate specimen collection. Gray indicates detection of only KIPyV or WUPyV, black indicates detection of KIPyV or WUPyV and a respiratory virus, and white indicates negative results for KIPyV or WUPyV.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: September 13, 2012
Page updated: September 13, 2012
Page reviewed: September 13, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.