Volume 18, Number 7—July 2012
Dispatch
Transmission of Bordetella holmesii during Pertussis Outbreak, Japan
Figure 2
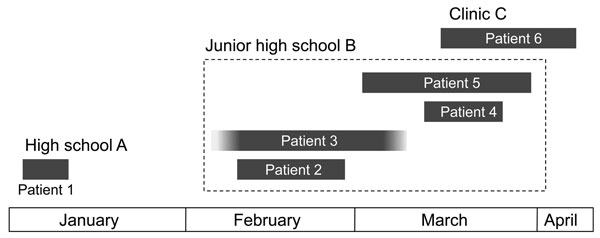
Figure 2. . . Epidemiologic linkage in 6 patients infected with Bordetella holmesii during pertussis outbreak, Japan, 2011. Duration of illness for each patient is shown as a gray box. Patient 3 provided unreliable information about the date of onset and recovery, but the patient’s cough lasted for >1 month. Epidemiologic linkage was observed between 5 patients (patients 2–6), but not for patient 1.
Page created: June 14, 2012
Page updated: June 14, 2012
Page reviewed: June 14, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.