Volume 19, Number 3—March 2013
Dispatch
Swine Influenza in Sri Lanka
Figure 2
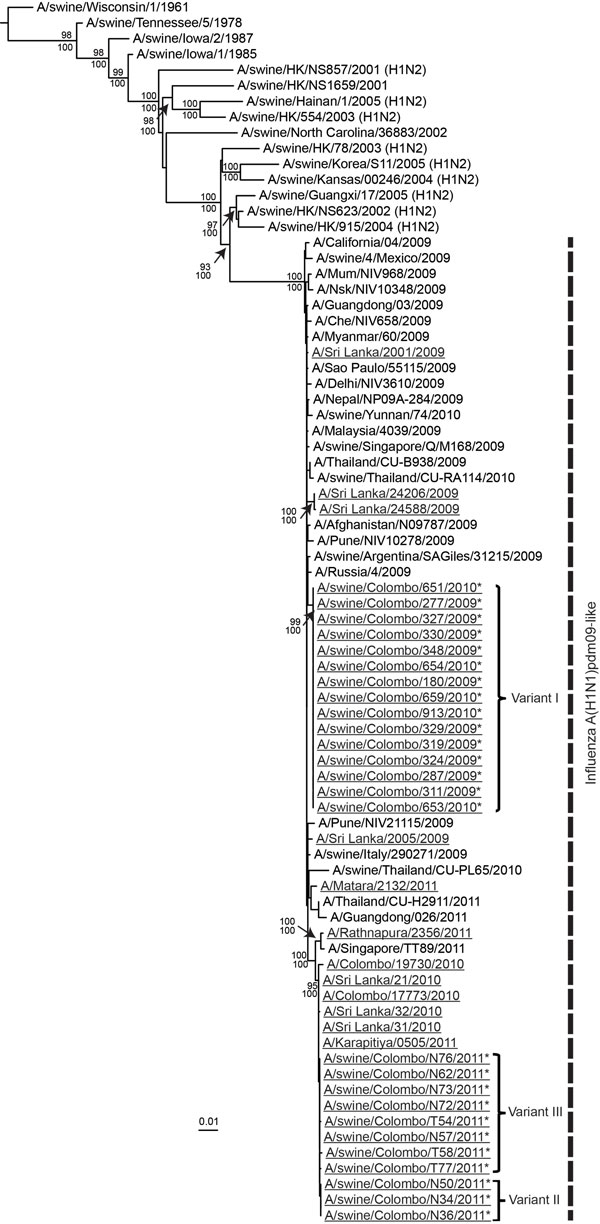
Figure 2. . . Phylogenetic relationship of the hemagglutinin 1 gene of the human and swine influenza A(H1N1)pdm09–like viruses isolated during 2009–2012 in Sri Lanka. Underlining indicates swine and human viruses characterized in this study; *indicates swine A(H1N1)pdm09 virus isolates. Nucleotide sequences from selected, related avian, equine, swine, and human virus strains available in GenBank are included for comparison. The phylogenetic tree was generated by the maximum-likelihood method and rooted to A/duck/Miyagi/66/77(H1N1) virus (Technical Appendix 1). Scale bar represents number of nucleotide substitutions per site. Vertical dashed line indicates influenza A(H1N1)pdm09–like virus lineage. Branch labels record the stability of the branches >500 bootstrap replicates. Numbers above and below branches indicate neighbor-joining bootstrap values and Bayesian posterior probabilities, respectively. Only bootstrap values ≥70% and Bayesian posterior probabilities ≥95% are shown. Three genetic variants with ≥1 aa difference in hemagglutinin 1 are indicated.