Volume 20, Number 12—December 2014
Research
Variably Protease-Sensitive Prionopathy, a Unique Prion Variant with Inefficient Transmission Properties
Figure 1
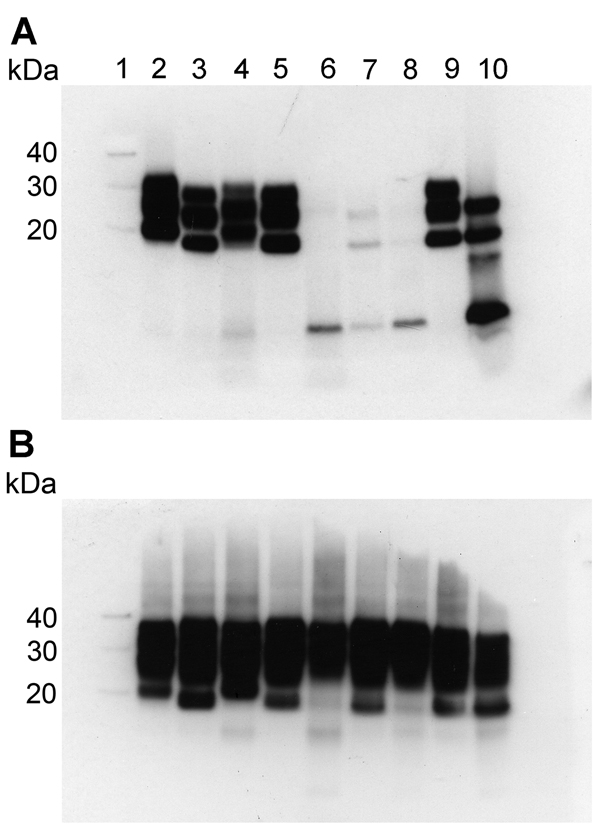
Figure 1. Western blot analysis of protease-resistant isoforms of PrP (PrPres) in extracts of frontal cortex tissue prepared from postmortem samples from 4 persons with sCJD and from 3 persons with VPSPr whose brain samples were used for experimental transmission studies in transgenic mice. Results are shown for extracts treated (A) and not treated (B) with proteinase K. All lanes were loaded with 5.0 μL of 10% (wt/vol) brain homogenate, except lanes 9 and 10 in (A), which were loaded with 1.5 μL and 20.0 μL, respectively. Blots were probed with Anti-Prion Protein Antibody monoclonal antibody 3F4 (Millipore, Watford, UK). Lane 1, molecular weight marker (sizes indicated at left in kDa); lane 2, sCJD subtype MM1; lane 3, sCJD subtype MM2; lane 4, sCJD subtype VV1; lane 5, sCJD subtype VV2; lane 6, VPSPr UK-VV; lane 7, VPSPr UK-MV; lane 8, VPSPr NL-VV; lane 9, diagnostic reference sample (sCJD subtype VV2); lane 10, diagnostic reference sample (VPSPr VV). MM, homozygous for methionine; MV, heterozygous for methionine/valine; NL-VV, patient from the Netherlands who had VPSPr and the codon 129VV genotype; sCJD, sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease; UK-VV and UK-MV, patients from the United Kingdom who had VPSPr and the codon 129VV and 129MV genotypes, respectively; VPSPr, variably protease-sensitive prionopathy; VV, homozygous for valine.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.