Volume 20, Number 12—December 2014
Research
Molecular Evolution of Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus
Figure 1
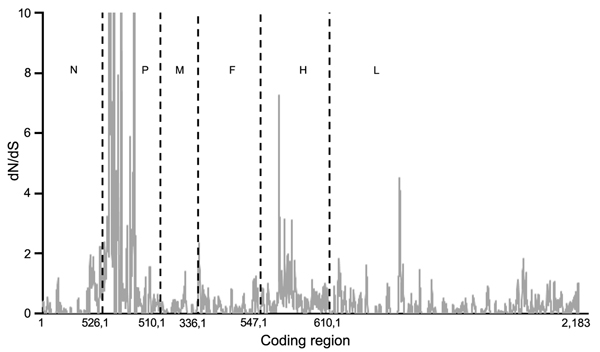
Figure 1. Mean ratios of nonsynonymous (dN) to synonymous (dS) substitutions per site of concatenated coding regions of peste des petits ruminants virus genome. Proportion of dS substitutions per potential dS site and proportion of dN substitutions per potential dN site were calculated by using the method of Nei and Gojobori (29) and the suite of nucleotide analysis program (www.hiv.lanl.gov). Vertical dashed lines indicate gene junctions with sliding windows of size = 5 codons. dN/dS values ≥ 10 are shown as 10. Numbers along baseline indicate coding regions (basepairs) of individual genes. N, nucleoprotein; P, phosphoprotein; M, matrix; F, fusion; H, hemagglutinin; L, large polymerase.
References
- Dhar P, Sreenivasa BP, Barrett T, Corteyn M, Singh RP, Bandyopadhyay SK. Recent epidemiology of peste des petits ruminants virus (PPRV). Vet Microbiol. 2002;88:153–9 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Banyard AC, Parida S, Batten C, Oura C, Kwiatek O, Libeau G. Global distribution of peste des petits ruminants virus and prospects for improved diagnosis and control. J Gen Virol. 2010;91:2885–97. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gibbs EP, Taylor WP, Lawman MJ, Bryant J. Classification of peste des petits ruminants virus as the fourth member of the genus Morbillivirus. Intervirology. 1979;11:268–74 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- de Swart RL, Duprex WP, Osterhaus AD. Rinderpest eradication: lessons for measles eradication? Curr Opin Virol. 2012;2:330–4.
- Baron MD, Parida S, Oura CA. Peste des petits ruminants: a suitable candidate for eradication? Vet Rec. 2011;169:16–21. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lembo T, Oura C, Parida S, Hoare R, Frost L, Fyumagwa R, Peste des petits ruminants infection among cattle and wildlife in northern Tanzania. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19:2037–40 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Balamurugan V, Sen A, Venkatesan G, Bhanot V, Yadav V, Bhanuprakash V, Peste des petits ruminants virus detected in tissues from an Asiatic lion (Panthera leo persica) belongs to Asian lineage IV. J Vet Sci. 2012;13:203–6 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Khalafalla AI, Saeed IK, Ali YH, Abdurrahman MB, Kwiatek O, Libeau G, An outbreak of peste des petits ruminants (PPR) in camels in the Sudan. Acta Trop. 2010;116:161–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Supporting livelihoods and supporting livelihoods and peste des petits ruminants (ppr) and small ruminant diseases control, 2013 [cited 2014 Sep 2]. http://www.fao.org/docrep/017/aq236e/aq236e00.htm
- Libeau G, Diallo A, Parida S. Evolutionary genetics underlying the spread of peste des petits ruminants virus. Anim Front. 2014;4:14–20. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Pybus OG, Rambaut A. Evolutionary analysis of the dynamics of viral infectious disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10:540–50. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Muniraju M, El Harrak M, Bao J, Ramasamy Parthiban AB, Banyard AC, Batten C, Complete genome sequence of a peste des petits ruminants virus recovered from an alpine goat during an outbreak in Morocco in 2008. Genome Announc. 2013;1:e00096–13.
- Chard LS, Bailey DS, Dash P, Banyard AC, Barrett T. Full genome sequences of two virulent strains of peste-des-petits ruminants virus, the Côte d’Ivoire 1989 and Nigeria 1976 strains. Virus Res. 2008;136:192–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Diallo A, Barrett T, Barbron M, Meyer G, Lefevre PC. Cloning of the nucleocapsid protein gene of peste-des-petits-ruminants virus: relationship to other morbilliviruses. J Gen Virol. 1994;75:233–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Furley CW, Taylor WP, Obi TU. An outbreak of peste des petits ruminants in a zoological collection. Vet Rec. 1987;121:443–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Taylor WP, al Busaidy S, Barrett T. The epidemiology of peste des petits ruminants in the Sultanate of Oman. Vet Microbiol. 1990;22:341–52. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Roeder PL, Abraham G, Kenfe G, Barrett T. Peste des petits ruminants in Ethiopian goats. Trop Anim Health Prod. 1994;26:69–73. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bao J, Wang Q, Parida S, Liu C, Zhang L, Zhao W, Complete genome sequence of a peste des petits ruminants virus recovered from wild bharal in Tibet, China. J Virol. 2012;86:10885–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wang Z, Bao J, Wu X, Liu Y, Li L, Liu C, Peste des petits ruminants virus in Tibet, China. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15:299–301. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bailey D, Banyard A, Dash P, Ozkul A, Barrett T. Full genome sequence of peste des petits ruminants virus, a member of the Morbillivirus genus. Virus Res. 2005;110:119–24. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hall TA. BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symposium Series. 1999;41:95–8.
- Pond SL, Frost SD, Muse SV. HyPhy: hypothesis testing using phylogenies. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:676–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Drummond AJ, Suchard MA, Xie D, Rambaut A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol Biol Evol. 2012;29:1969–73. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Miller MA, Pfeiffer W, Schwartz T. Creating the CIPRES science gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. Presented at: Proceedings of the Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE); 2010 Nov 14; New Orleans, Louisiana, USA; p. 1– 8.
- Posada D. jModelTest: phylogenetic model averaging. Mol Biol Evol. 2008;25:1253–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lemey P, Rambaut A, Drummond AJ, Suchard MA. Bayesian phylogeography finds its roots. PLOS Comput Biol. 2009;5:e1000520. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Radecke F, Spielhofer P, Schneider H, Kaelin K, Huber M, Dotsch C, Rescue of measles viruses from cloned DNA. EMBO J. 1995;14:5773–84 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nei M, Gojobori T. Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol Biol Evol. 1986;3:418–26 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Han GZ, Worobey M. Homologous recombination in negative sense RNA viruses. Viruses. 2011;3:1358–73. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Denison MR, Graham RL, Donaldson EF, Eckerle LD, Baric RS. Coronaviruses: an RNA proofreading machine regulates replication fidelity and diversity. RNA Biol. 2011;8:270–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pomeroy LW, Bjornstad ON, Holmes EC. The evolutionary and epidemiological dynamics of the paramyxoviridae. J Mol Evol. 2008;66:98–106. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Furuse Y, Suzuki A, Oshitani H. Origin of measles virus: divergence from rinderpest virus between the 11th and 12th centuries. Virol J. 2010;7:52. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wertheim JO, Kosakovsky Pond SL. Purifying selection can obscure the ancient age of viral lineages. Mol Biol Evol. 2011;28:3355–65. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jenkins GM, Rambaut A, Pybus OG, Holmes EC. Rates of molecular evolution in RNA viruses: a quantitative phylogenetic analysis. J Mol Evol. 2002;54:156–65. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gargadennec L, Lalanne A. Peste des petits ruminants [in French]. Bulletin des Services Zootechniques et des Epizzoties de l’Afrique Occidentale Francaise. 1942;5:16–21.
- Biek R, Drummond AJ, Poss M. A virus reveals population structure and recent demographic history of its carnivore host. Science. 2006;311:538–41. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lemey P, Suchard M, Rambaut A. Reconstructing the initial global spread of a human influenza pandemic: a Bayesian spatial-temporal model for the global spread of H1N1pdm. PLoS Curr. 2009;1:RRN1031. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Diallo A. Rinderpest and peste des petits ruminants. Constant threats against livestock in many countries [in French]. Impact Sci Soc. 1988;150:191–204.
- Sen A, Saravanan P, Balamurugan V, Rajak KK, Sudhakar SB, Bhanuprakash V, Vaccines against peste des petits ruminants virus. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2010;9:785–96. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1Preliminary results were presented at the 15th International Negative Strand Virus Meeting, June 16–21, 2013, Granada, Spain.