Volume 20, Number 12—December 2014
Dispatch
Equine Influenza A(H3N8) Virus Infection in Cats
Figure 1
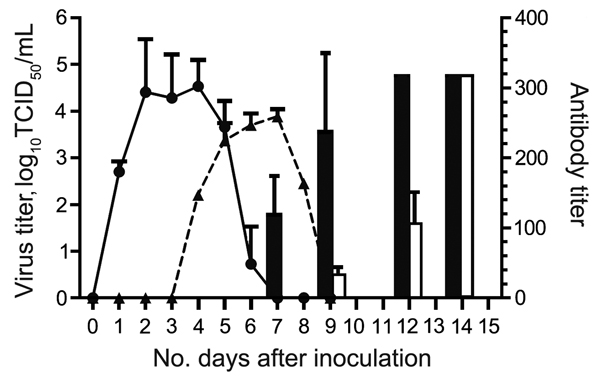
Figure 1. Results of virus titration and hemagglutination-inhibition assay for the cohort of cats inoculated with equine influenza A(H3N8) virus and the contact cohort. Virus shedding was titrated in MDCK cells. Virus titer is shown as log10 median tissue culture infective dose (TCID50) (solid line and circles, inoculated cohort; dashed line and triangles, contact cohort). Hemagglutination-inhibition assay of serum samples was conducted by using 1% horse erythrocytes (black bars, inoculated; white bars, contact cohort). Error bars indicate SEM.
1These authors contributed equally to this work.
Page created: November 19, 2014
Page updated: November 19, 2014
Page reviewed: November 19, 2014
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.