Volume 20, Number 3—March 2014
Research
High-level Relatedness among Mycobacterium abscessus subsp. massiliense Strains from Widely Separated Outbreaks
Figure 1
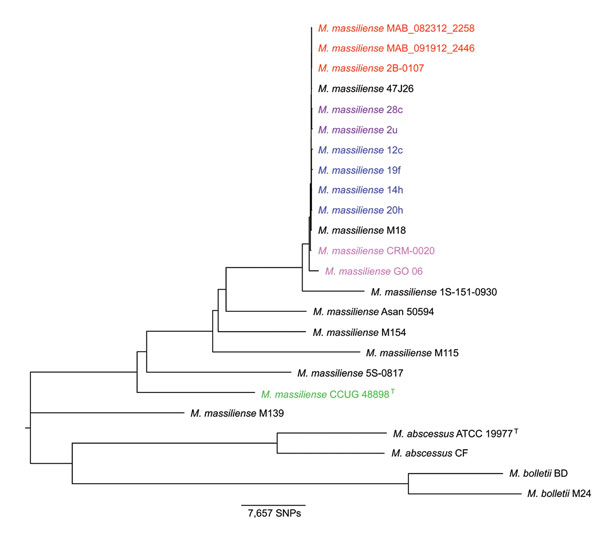
Figure 1. Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on whole-genome multiple alignment of 24 Mycobacterium abscessus group genomesGenomes in Table 1 were aligned by using Mugsy (22), core segments of the alignment were identified by using Phylomark (23), and resulting concatenated nucleotide sequences were used for construction of the midpoint-rooted neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree by using MEGA (24)Strains from an outbreak of Mabscessus subspmassiliense infections at a cystic fibrosis center in Seattle, Washington, USA, are indicated in red; strains from an outbreak of Mabscessus subspmassiliense infections at a cystic fibrosis center in Papworth, UK, are indicated in blue (cluster 1) and purple (cluster 2); strains from Brazil are indicated in magenta; and the Mabscessus subspmassiliense type strain is indicated in greenBoostrap values obtained after 100 iterations were ≥97 for all nodes of the tree except 70 for the node separating strain M115 from the outbreak cluster and 40 and 41 for 2 nodes within the Papworth cluster 1 (6)SNPs, single-nucleotide polymorphisms.
References
- Levy I, Grisaru-Soen G, Lerner-Geva L, Kerem E, Blau H, Bentur L, Multicenter cross-sectional study of nontuberculous mycobacterial infections among cystic fibrosis patients, Israel. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:378–84 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Olivier KN, Weber DJ, Wallace RJ Jr, Faiz AR, Lee JH, Zhang Y, Nontuberculous mycobacteria. I: multicenter prevalence study in cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;167:828–34. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Roux AL, Catherinot E, Ripoll F, Soismier N, Macheras E, Ravilly S, Multicenter study of prevalence of nontuberculous mycobacteria in patients with cystic fibrosis in France. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:4124–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sermet-Gaudelus I, Le Bourgeois M, Pierre-Audigier C, Offredo C, Guillemot D, Halley S, Mycobacterium abscessus and children with cystic fibrosis. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9:1587–91. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Aitken ML, Limaye A, Pottinger P, Whimbey E, Goss CH, Tonelli MR, Respiratory outbreak of Mycobacterium abscessus subspecies massiliense in a lung transplant and cystic fibrosis center. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;185:231–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bryant JM, Grogono DM, Greaves D, Foweraker J, Roddick I, Inns T, Whole-genome sequencing to identify transmission of Mycobacterium abscessus between patients with cystic fibrosis: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2013;381:1551–60 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Davidson RM, Reynolds PR, Farias-Hesson E, Duarte RS, Jackson M, Strong M. Genome sequence of an epidemic isolate of Mycobacterium abscessus subsp. bolletii from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Genome Announc. 2013;1:e00617–13.
- Raiol T, Ribeiro GM, Maranhao AQ, Bocca AL, Silva-Pereira I, Junqueira-Kipnis AP, Complete genome sequence of Mycobacterium massiliense. J Bacteriol. 2012;194:5455. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chan J, Halachev M, Yates E, Smith G, Pallen M. Whole-genome sequence of the emerging pathogen Mycobacterium abscessus strain 47J26. J Bacteriol. 2012;194:549. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ngeow YF, Wong YL, Tan JL, Arumugam R, Wong GJ, Ong CS, Genome sequence of Mycobacterium massiliense M18, isolated from a lymph node biopsy specimen. J Bacteriol. 2012;194:4125. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ngeow YF, Wong YL, Lokanathan N, Wong GJ, Ong CS, Ng KP, Genomic analysis of Mycobacterium massiliense strain M115, an isolate from human sputum. J Bacteriol. 2012;194:4786 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ngeow YF, Wee WY, Wong YL, Tan JL, Ongi CS, Ng KP, Genomic analysis of Mycobacterium abscessus strain M139, which has an ambiguous subspecies taxonomic position. J Bacteriol. 2012;194:6002–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Choo SW, Wong YL, Tan JL, Ong CS, Wong GJ, Ng KP, Annotated genome sequence of Mycobacterium massiliense strain M154, belonging to the recently created taxon Mycobacterium abscessus subsp. bolletii comb. nov. J Bacteriol. 2012;194:4778. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kim BJ, Kim BR, Hong SH, Seok SH, Kook YH. Complete genome sequence of Mycobacterium massiliense clinical strain Asan 50594, belonging to the type II genotype. Genome Announc. 2013;1:e00429–13.
- Tettelin H, Sampaio EP, Daugherty SC, Hine E, Riley DR, Sadzewicz L, Genomic insights into the emerging human pathogen Mycobacterium massiliense. J Bacteriol. 2012;194:5450 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Adékambi T, Reynaud-Gaubert M, Greub G, Gevaudan MJ, La Scola B, Raoult D, Amoebal coculture of “Mycobacterium massiliense” sp. nov. from the sputum of a patient with hemoptoic pneumonia. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:5493–501 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pawlik A, Garnier G, Orgeur M, Tong P, Lohan A, Le Chevalier F, Identification and characterization of the genetic changes responsible for the characteristic smooth-to-rough morphotype alterations of clinically persistent Mycobacterium abscessus. Mol Microbiol. 2013;3:•••; Epub ahead of print and.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ripoll F, Pasek S, Schenowitz C, Dossat C, Barbe V, Rottman M, Non mycobacterial virulence genes in the genome of the emerging pathogen Mycobacterium abscessus. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e5660. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Choi GE, Cho YJ, Koh WJ, Chun J, Cho SN, Shin SJ. Draft genome sequence of Mycobacterium abscessus subsp. bolletii BD(T). J Bacteriol. 2012;194:2756–7 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wong YL, Choo SW, Tan JL, Ong CS, Ng KP, Ngeow YF. Draft genome sequence of Mycobacterium bolletii strain M24, a rapidly growing mycobacterium of contentious taxonomic status. J Bacteriol. 2012;194:4475 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zerbino DR, Birney E. Velvet: algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 2008;18:821–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Angiuoli SV, Salzberg SL. Mugsy: fast multiple alignment of closely related whole genomes. Bioinformatics. 2011;27:334–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sahl JW, Matalka MN, Rasko DA. Phylomark, a tool to identify conserved phylogenetic markers from whole-genome alignments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012;78:4884–92. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011;28:2731–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Li H, Durbin R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:1754–60. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, The Genome Analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010;20:1297–303. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Macheras E, Roux AL, Ripoll F, Sivadon-Tardy V, Gutierrez C, Gaillard JL, Inaccuracy of single-target sequencing for discriminating species of the Mycobacterium abscessus group. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:2596–600. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Adékambi T, Colson P, Drancourt M. rpoB-based identification of nonpigmented and late-pigmenting rapidly growing mycobacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41:5699–708. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zelazny AM, Root JM, Shea YR, Colombo RE, Shamputa IC, Stock F, Cohort study of molecular identification and typing of Mycobacterium abscessus, Mycobacterium massiliense, and Mycobacterium bolletii. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:1985–95. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Macheras E, Roux AL, Bastian S, Leao SC, Palaci M, Sivadon-Tardy V, Multilocus sequence analysis and rpoB sequencing of Mycobacterium abscessus (sensu lato) strains. J Clin Microbiol. 2011;49:491–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994;22:4673–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Duarte RS, Lourenco MC, Fonseca Lde S, Leao SC, Amorim Ede L, Rocha IL, Epidemic of postsurgical infections caused by Mycobacterium massiliense. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:2149–55. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Leão SC, Viana-Niero C, Matsumoto CK, Lima KV, Lopes ML, Palaci M, Epidemic of surgical-site infections by a single clone of rapidly growing mycobacteria in Brazil. Future Microbiol. 2010;5:971–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Varela C, Rittmann D, Singh A, Krumbach K, Bhatt K, Eggeling L, MmpL genes are associated with mycolic acid metabolism in mycobacteria and corynebacteria. Chem Biol. 2012;19:498–506. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Leão SC, Matsumoto CK, Carneiro A, Ramos RT, Nogueira CL, Lima JD Jr, The detection and sequencing of a broad-host-range conjugative IncP-1beta plasmid in an epidemic strain of Mycobacterium abscessus subsp. bolletii. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e60746. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wallace RJ Jr, Meier A, Brown BA, Zhang Y, Sander P, Onyi GO, Genetic basis for clarithromycin resistance among isolates of Mycobacterium chelonae and Mycobacterium abscessus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1996;40:1676–81 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Prammananan T, Sander P, Brown BA, Frischkorn K, Onyi GO, Zhang Y, A single 16S ribosomal RNA substitution is responsible for resistance to amikacin and other 2-deoxystreptamine aminoglycosides in Mycobacterium abscessus and Mycobacterium chelonae. J Infect Dis. 1998;177:1573–81. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shallom SJ, Gardina PJ, Myers TG, Sebastian Y, Conville P, Calhoun LB, New rapid scheme for distinguishing the subspecies of the Mycobacterium abscessus group and identification of Mycobacterium massiliense with inducible clarithromycin resistance. J Clin Microbiol. 2013;51:2943–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Koh WJ, Jeon K, Lee NY, Kim BJ, Kook YH, Lee SH, Clinical significance of differentiation of Mycobacterium massiliense from Mycobacterium abscessus. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183:405–10. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bange FC, Brown BA, Smaczny C, Wallace RJ Jr, Bottger EC. Lack of transmission of Mycobacterium abscessus among patients with cystic fibrosis attending a single clinic. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:1648–50. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar